Sikanna Katu Pirka Cikoykip Okay.
Sikanna katu pirka cikoykip okay.
(Dragons are beautiful creatures.)
reblog if you are a NERD who loves DRAGONS
I MEAN…

Who

Doesnt

like dragons?
They can be loyal

or they can be firce

How can you not love dragons?

They are like huge cats
-
 redhoodscorvid reblogged this · 4 months ago
redhoodscorvid reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 dia-viller reblogged this · 4 months ago
dia-viller reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 dia-viller liked this · 4 months ago
dia-viller liked this · 4 months ago -
 the-letter-horror-lover liked this · 5 months ago
the-letter-horror-lover liked this · 5 months ago -
 enhasaur reblogged this · 5 months ago
enhasaur reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 enhasaur liked this · 5 months ago
enhasaur liked this · 5 months ago -
 loonataeworld reblogged this · 7 months ago
loonataeworld reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 loonataeworld liked this · 7 months ago
loonataeworld liked this · 7 months ago -
 slitzy-the-animaldrones liked this · 8 months ago
slitzy-the-animaldrones liked this · 8 months ago -
 senyatiryz liked this · 8 months ago
senyatiryz liked this · 8 months ago -
 autisticpositivity reblogged this · 9 months ago
autisticpositivity reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 arbielikestrains liked this · 10 months ago
arbielikestrains liked this · 10 months ago -
 discardedpawns liked this · 10 months ago
discardedpawns liked this · 10 months ago -
 fandomsandwriting1 reblogged this · 10 months ago
fandomsandwriting1 reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 fandomsandwriting1 liked this · 10 months ago
fandomsandwriting1 liked this · 10 months ago -
 ammonitetheseaserpent reblogged this · 10 months ago
ammonitetheseaserpent reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 kitzani reblogged this · 10 months ago
kitzani reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 glitchylaptop liked this · 10 months ago
glitchylaptop liked this · 10 months ago -
 ghost-the-bean reblogged this · 10 months ago
ghost-the-bean reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 glitchylaptop reblogged this · 10 months ago
glitchylaptop reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 dizzydreamerzzz reblogged this · 1 year ago
dizzydreamerzzz reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 wyvern-kat liked this · 1 year ago
wyvern-kat liked this · 1 year ago -
 psychicsongcollective liked this · 1 year ago
psychicsongcollective liked this · 1 year ago -
 ethuilielcyneburg reblogged this · 1 year ago
ethuilielcyneburg reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 emeraldinerosefaedragon reblogged this · 1 year ago
emeraldinerosefaedragon reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 emeraldinerosefaedragon liked this · 1 year ago
emeraldinerosefaedragon liked this · 1 year ago -
 thenookspace reblogged this · 1 year ago
thenookspace reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rooksnooks liked this · 1 year ago
rooksnooks liked this · 1 year ago -
 des8pudels8kern reblogged this · 1 year ago
des8pudels8kern reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 4n-3n19m4 reblogged this · 1 year ago
4n-3n19m4 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 4n-3n19m4 liked this · 1 year ago
4n-3n19m4 liked this · 1 year ago -
 authorityofboredom liked this · 1 year ago
authorityofboredom liked this · 1 year ago -
 raviotheraviolis liked this · 1 year ago
raviotheraviolis liked this · 1 year ago -
 konoharu liked this · 1 year ago
konoharu liked this · 1 year ago -
 filkovaariik liked this · 1 year ago
filkovaariik liked this · 1 year ago -
 bellamy-blakesgirl liked this · 1 year ago
bellamy-blakesgirl liked this · 1 year ago -
 w00p liked this · 1 year ago
w00p liked this · 1 year ago -
 fire-in-the-dingo liked this · 1 year ago
fire-in-the-dingo liked this · 1 year ago
More Posts from Oroichonno
Sukka kuy wa uyka kuy henne anne netopa eramat. Ingar mak e=ki.
(Acid urine and alkaline urine do not mean a healthy body. Watch what you do.) If you hear about seemingly beneficial claims for or against a product, please look carefully into them & examine.
Scishow: Is Alkaline Water Really Better For You?
A new health trend is claiming that it can rebalance your internal chemistry and help prevent cancers and bone loss, but what are the real health benefits of drinking alkaline water?
Hosted by: Olivia Gordon
Mokor katu ari e=pirio en e=tusa ruwe okay.
(Sleep positions [forms] for you to heal your injuries.) This post should help you if you fall ill or sick.
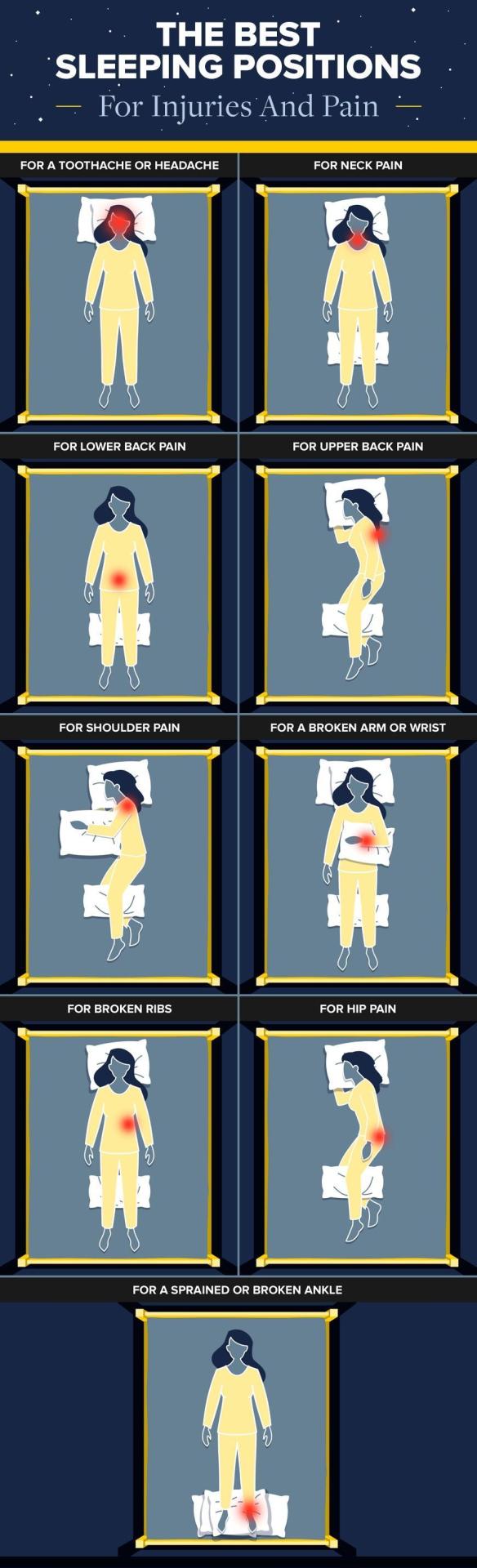
The best sleeping positions when you are injured.
We should keep these in mind when we wish to travel beyond the stars, great especially for extraterrestrial exploration. As it turns out and as this touches on, astronauts and aquanauts share much of the same kind of training as well as tech for their work.
Earth’s Ocean and Beyond

Image Credit: NOAA
Earth’s ocean has been the backdrop for ancient epics, tales of fictional fish and numerous scientific discoveries. It was, and will always be, a significant piece of the Earth’s story. Most of the ocean is unexplored– about 95% of this underwater realm is unseen by human eyes (NOAA). There is only one global Ocean. In fact, the ocean represents over 70% of the Earth’s surface and contains 96.5% of the Earth’s water.
We and the NOAA Office of Ocean Exploration and Research work together alongside organizations like the Schmidt Ocean Institute and Ocean Exploration Trust to better understand our oceans and its processes. While space may be the final frontier, understanding our own planet helps scientists as they explore space and study how our universe came to be.
On #WorldOceansDay let’s explore how Earth’s ocean informs our research throughout the solar system.
Earth and Exoplanets

“In interpreting what we see elsewhere in the solar system and universe, we always compare with phenomena that we already know of on Earth…We work from the familiar toward the unknown.” - Norman Kuring, NASA Goddard
We know of only one living planet: our own. As we move to the next stage in the search for alien life, the effort will require the expertise of scientists of all disciplines. However, the knowledge and tools NASA has developed to study life on Earth will also be one of the greatest assets to the quest.
The photo above shows what Earth would look like at a resolution of 3 pixels, the same that exoplanet-discovering missions would see. What should we look for, in the search of other planets like our own? What are the unmistakable signs of life, even if it comes in a form we don’t fully understand? Liquid water; every cell we know of – even bacteria around deep-sea vents that exist without sunlight – requires water.
Phytoplankton (Algae) Bloom vs. Atmosphere of Jupiter

Jupiter’s storms are mesmerizing in their beauty, captured in many gorgeous photos throughout the decades from missions like Voyager 1 and Juno. The ethereal swirls of Jupiter are the result of fluids in motion on a rotating body, which might come as a surprise, since its atmosphere is made of gas!
The eddies in Jupiter’s clouds appear very similar to those found in Earth’s ocean, like in the phytoplankton (or algae) bloom in the Baltic Sea, pictured above. The bloom was swept up in a vortex, just a part of how the ocean moves heat, carbon, and nutrients around the planet. Blooms like this, however, are not all beauty - they create “dead zones” in the areas where they grow, blooming and decaying at such a high rate that they consume all the oxygen in the water around them.
Arctic Sea Ice and Europa Ice Crust

While the Arctic (North Pole) and the Antarctic (South Pole) are “polar opposites,” there is one huge difference between the North and South Poles– land mass. The Arctic is ocean surrounded by land, while the Antarctic is land surrounded by ocean. The North Pole is located in the middle of the Arctic Ocean amid waters that are almost permanently covered with constantly shifting sea ice.
By studying this sea ice, scientists can research its impact on Earth system and even formation processes on other bodies like Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter. For example, it is possible that the reddish surface features on Europa’s ice may have communicated with a global subsurface ocean layer during or after their formation.
Aquanauts and Astronauts

As new missions are being developed, scientists are using Earth as a testbed. Just as prototypes for our Mars rovers made their trial runs on Earth’s deserts, researchers are testing both hypotheses and technology on our oceans and extreme environments.
NEEMO, our Extreme Environment Mission Operations project, is an analog mission that sends groups of astronauts, engineers and scientists to live in Aquarius, the world’s only undersea research station located off the Florida Keys, 62 feet (19 meters) below the surface. Much like space, the undersea world is a hostile, alien place for humans to live. NEEMO crew members, known as aquanauts, experience some of the same challenges there that they would on a distant asteroid, planet or moon.
Deep-sea Robotic Exploration and Space Robotic Exploration

Video credit: Deep Sea Robotics/Schmidt Ocean Institute and Mars Curiosity rover/NASA
From mapping the seafloor through bathymetry to collecting samples on the surface of Mars, researchers are utilizing new technologies more than ever to explore. Satellite and robotic technology allow us to explore where humans may not be able to– yet. They teach us valuable lessons about the extreme and changing environments, science, as well as provide a platform to test new technologies.
Jezero Crater and Dvina River Delta, Arkhangelsk, Russia/Mars Delta

River deltas, the point where a river meets the ocean, are sites of rich sediment and incredible biodiversity. The nutrients that rivers carry to the coastlines make a fertile place for fish and shellfish to lay their eggs.
The Jezero crater on Mars (pictured in false-color on the right) has been selected as the Mars2020 landing site, and has a structure that looks much like a river delta here on Earth! Pictures from our Mars Global Surveyor orbiter show eroded ancient deposits of transported sediment long since hardened into interweaving, curved ridges of layered rock. This is one of many hints that Mars was once covered in an ancient ocean that had more water than the Arctic Ocean. Studying these deltas on Earth helps us spot them on other planets, and learning about the ocean that was once on Mars informs how our own formed.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
These would be handy to know that space programs can be useful for improvement of life on Earth. After all, multiple groups would do well to learn from this & make more discoveries.
6 Ways NASA Technology Makes You Healthier
An important part of our mission is keeping astronauts strong and healthy during stays in space, but did you know that our technology also helps keep you healthy? And the origins of these space innovations aren’t always what you’d expect.
As we release the latest edition of NASA Spinoff, our yearly publication that celebrates all the ways NASA technology benefits us here on Earth, let’s look at some ways NASA is improving wellness for astronauts—and everyone else.
1. Weightless weight-lifting

Without gravity to work against, astronauts lose bone and muscle mass in space. To fight it, they work out regularly. But to get them a good burn, we had to get creative. After all, pumping iron doesn’t do much good when the weights float.
The solution? Elastic resistance. Inventor Paul Francis was already working on a portable home gym that relied on spiral-shaped springs made of an elastic material. He thought the same idea would work on the space station and after additional development and extensive testing, we agreed.
Our Interim Resistive Exercise Device launched in 2000 to help keep astronauts fit. And Francis’ original plan took off too. The technology perfected for NASA is at the heart of the Bowflex Revolution as well as a new line of handheld devices called OYO DoubleFlex, both of which enable an intensive—and extensive—workout, right at home.
2. Polymer coating keeps hearts beating

A key ingredient in a lifesaving treatment for many patients with congestive heart failure is made from a material a NASA researcher stumbled upon while working on a supersonic jet in the 1990s.
Today, a special kind of pacemaker that helps synchronize the left and right sides of the heart utilizes the unique substance known as LaRC-SI. The strong material can be cast extremely thin, which makes it easier to insert in the tightly twisted veins of the heart, and because it insulates so well, the pacemaker’s electric pulses go exactly where they should.
Since it was approved by the FDA in 2009, the device has been implanted hundreds of thousands of times.
3. Sutures strong enough for interplanetary transport

Many people mistakenly think we created Teflon. Not true: DuPont invented the unique polymer in 1938. But an innovative new way to use the material was developed to help us transport samples back from Mars and now aids in stitching up surgery patients.
Our scientists would love to get pristine Martian samples into our labs for more advanced testing. One complicating factor? The red dust makes it hard to get a clean seal on the sample container. That means the sample could get contaminated on its way back to Earth.
The team building the cannister had an idea, but they needed a material with very specific properties to make it work. They decided to use Polytetrafluoroethylene (that’s the scientific name for Teflon), which works really well in space.
The material we commonly recognize as Teflon starts as a powder, and to transform it into a nonstick coating, the powder gets processed a certain way. But process it differently, and you can get all kinds of different results.
For our Mars sample return cannister prototype, the powder was compressed at high pressures into a block, which was then forced through an extruder. (Imagine pressing playdough through a mold). It had never been done before, but the end result was durable, flexible and extremely thin: exactly what we needed.
And since the material can be implanted safely in the human body—it was also perfect as super strong sutures for after surgery.
4. Plant pots that clean the air

It may surprise you, but the most polluted air you breathe is likely the air inside your home and office. That’s especially true these days with energy-efficient insulation: the hot air gets sealed in, but so do any toxins coming off the paint, furniture, cooking gas, etc.
This was a problem NASA began worrying about decades ago, when we started planning for long duration space missions. After all, there’s no environment more insulated than a spaceship flying through the vacuum of space.
On Earth, plants are a big part of the “life support” system cleaning our air, so we wondered if they could do the same indoors or in space.
The results from extensive research surprised us: we learned the most important air scrubbing happens not through a plant’s leaves, but around its roots. And now you can get the cleanest air out of your houseplants by using a special plant pot, available online, developed with that finding in mind: it maximizes air flow through the soil, multiplying the plant’s ability to clean your air.
5. Gas sensor detects pollution from overhead

Although this next innovation wasn’t created with pollution in mind, it’s now helping keep an eye on one of the biggest greenhouse gasses: methane.
We created this tiny methane “sniffer” to help us look for signs of life on Mars. On Earth, the biggest source of methane is actually bacteria, so when one of our telescopes on the ground caught a glimpse of the gas on Mars, we knew we needed to take a closer look.
We sent this new, extremely sensitive sensor on the Curiosity Rover, but we knew it could also be put to good use here on our home planet. We adapted it, and today it gets mounted on drones and cars to quickly and accurately detect gas leaks and methane emissions from pipelines, oil wells and more.
The sensor can also be used to better study emissions from swamps and other natural sources, to better understand and perhaps mitigate their effects on climate change.
6. DNA “paint” highlights cellular damage

There’s been a lot of news lately about DNA editing: can genes be changed safely to make people healthier? Should they be?
As scientists and ethicists tackle these big questions, they need to be sure they know exactly what’s changing in the genome when they use the editing tools that already exist.
Well, thanks to a tool NASA helped create, we can actually highlight any abnormalities in the genetic code with special fluorescent “paint.”
But that’s not all the “paint” can do. We actually created it to better understand any genetic damage our astronauts incurred during their time in space, where radiation levels are far higher than on Earth. Down here, it could help do the same. For example, it can help doctors select the right cancer treatment by identifying the exact mutation in cancer cells.
You can learn more about all these innovations, and dozens more, in the 2019 edition of NASA Spinoff. Read it online or request a limited quantity print copy and we’ll mail it to you!
Good to know, especially in the wild.
I swear to god raspberries get moldy so fuckin fast you just look at them wrong and they immediately go bad
