
1575 posts
Mettmann: Fundsttte Des Neanderthalers
Mettmann: Fundstätte des Neanderthalers
- Deutsch/German -
Der Kreis Mettmann ist weltberühmt – auch wenn wohl kaum jemand in Afrika oder Amerika den Namen der Region kennt.

Der Name des prominentesten Bewohners ist jedoch in aller Munde: 1856 wurden hier die sterblichen Überreste des Neandertalers gefunden. Der Kreis Mettmann ist damit der erste Fundort eines Neandertalers weltweit.

250.000 Jahre lang lebten die Neandertaler in Europa, angepasst an die rauen Lebensbedingungen der Eiszeit. Dass es sie überhaupt gab, deckte erst der Fund ihrer Überreste auf: 40.000 Jahre vor unserer Zeitrechnung stapft eine Gruppe von Menschen über die Hochebene unweit der Düssel.

Ihre Stirn ist flach, ihre Augen sind überwölbt von dicken Wülsten. Sie tragen Felle am Leib als Schutz gegen den eisigen Wind. Ihre Füße wandern über Steine und hart gefrorene Erde. Die Eiszeit hat Europa im Griff.

Da es in der kühlen Umgebung nur wenige essbare Pflanzen gab, sind die kleinen Stammesverbände vermutlich hinter den Nahrung suchenden Tierherden der Eiszeit her gewandert.

Eine Höhle wurde von der Düssel und kleineren Zuflüssen in Millionen von Jahren aus den Kalksteinfelsen des steinernen Plateaus herausgespült. Einer dieser Frühmenschen wurde in dieser Höhle etwa 20 Meter oberhalb der Düssel bestattet. Seine 16 noch erhaltenen Knochen sind heute im Neandertalmuseum zu sehen.

Die Entdeckung des Skeletts verdanken die Forscher dem Kalkabbau, der im 19. Jahrhundert im Zuge der Industrialisierung einsetzte. Noch heute wackeln im Neandertal gelegentlich die Wände, wenn im letzten verbliebenen Kalksteinwerk eine Sprengung durchgeführt wird.

Der Kalkstein wurde Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts zu einem begehrten Rohstoff. Er wird bei der Stahlherstellung in der Eisenindustrie und als Baustoff benötigt. 1849 beginnt der Abbau im Neandertal im großen Maßstab.

Ihren Namen hat die Region dem Theologen und Kirchenlied-Schreiber Joachim Neander zu verdanken, der im 17. Jahrhundert in der damals engen und tiefen Schlucht Gottesdienste abhielt und Kirchenlieder komponierte. Unter Kennern war das Neandertal bereits schon lange für seine reichen diluvialen Ablagerungen bekannt.

Während der Arbeiten stießen Bergleute in den Höhlen auf die Skelettteile. Diese Höhle war 3 m breit, 5 m lang und 3 m hoch. Die Arbeiter räumten die Grotte frei und beachteten die Knochenfunde zunächst nur beiläufig, weil Knochen ausgestorbener Tiere hier sehr häufig gefunden wurden.

Für die Arbeiter sahen die Knochen denen von Höhlenbären ähnlich und deshalb warfen sie sie weg. An den Knochen kann man heute noch deutlich die Beschädigungen erkennen, welche die Arbeiter mit Spitzhacken dem Neandertaler zufügten.

Dass die Knochen im anatomischen Verband gelegen haben, zeigen die gut erkennbaren Hackspuren. Beim Freilegen wurde nämlich die linke hälfte der Hüfte und der Gelenkkopf des Oberschenkels beschädigt. Die hinterbliebene Furche geht fließend von einem Knochen in den anderen über.

Zufällig fielen die fossilen Funde dem Mitbesitzer des Neandertaler Steinbruchs Wilhelm Beckershoff auf, der gerade vor Ort war. Sein Geschäftspartner Friedrich Wilhelm Pieper übergab sie dem örtlich bekannten Naturforscher Dr. Johann Carl Fuhlrott. Fuhlrott sah sich die Stücke an und bemerkte jedoch schnell, dass dieses Skelett einem diluvialen Vor- bzw. Urmenschen zugehörig sein musste.

Zwischen 1997 und 2000 wurden im Neandertal von Ralf Schmitz und Jürgen Thissen Nachgrabungen durchgeführt, bei denen 62 weitere Knochenfragmente gefunden wurden. Darunter befanden sich sechs Neandertalerzähne, die zum Fund von 1856 gehören könnten.

Einige Knochenfragmente passten direkt an das Skelett von 1856 an. Seit der Nachgrabung liegen so viele Knochen vor, dass von mindestens einem weiteren adulten und einem subadulten Neandertaler ausgegangen wird.

Eng und tief ist das Tal heute nicht mehr und auch die Wasserfälle, Klippen und prächtigen Höhlen sind weitgehend verschwunden. Der Fortschritt ist wichtiger als die Natur. Als das Gebiet 1921 unter Naturschutz gestellt wird, ist aus der steilen Schlucht ein weites, baumloses Tal geworden.

Millionen Tonnen Gestein sind im Zuge der Industrialisierung abgetragen worden. Die Feldhofer Grotten und den Lieblingsplatz von Joachim Neander gibt es nicht mehr. Nichts erinnert mehr an den Lebensraum des Neandertalers.

Die Sprengungen zerstörten die malerische Felsenschlucht vollständig. Dafür haben Buchen-, Hainbuchen- und Schluchtwälder die Region erobert, die die Hügel und Hänge bewachsen und die ehemaligen Steinbrüche in sattes Grün tauchen.

Landschaftsarchitekten haben den Fundort jedoch als archäologischen Garten inszeniert, der die wechselvolle Geschichte des Tals erzählt. Wer mag, kann sich alle Zeugnisse der Fundstelle auch durch ein Audiosystem erklären lassen.

An der Fundstelle stehen jetzt ein paar Steinliegen. Und es sind ein paar Stangen aufgestellt. Wirklich informativ wird der Ort aber durch die zahlreichen Infos aus der App oder via Kopfhörer, für die es zahlreiche Gelegenheiten zum einstöpseln gibt.

Viele Informationen sind über Kopfhörer zu hören, die ihr für den Rundgang ausgeliehen bekommt. Wer das alles auf seinem Handy hören will, kann sich seit einiger Zeit auch eine Neanderthal – Museums – App herunterladen, die zu allen Punkten coole Informationen hat.

Positiv überraschten uns die zahlreichen Fakten, die auf so spielerische Weise aufbereitet werden. Wer in der Region unterwegs ist, sollte dort unbedingt mal vorbeischauen. Achtung: die Funstelle schließt früher als das Museum.

Weitergehende Informationen bietet das 1996 eröffnete Neanderthal-Museum. Der markante spiralförmige Bau liegt nur wenige hundert Meter von der Fundstelle entfernt. Ein gepflasterter Weg führt als Zeitstrahl bis zur Stelle des historischen Fundortes.

Bei unserem Besuch wurde an der Fundstelle kein Eintritt erhoben!
-
 logi1974 liked this · 4 years ago
logi1974 liked this · 4 years ago
More Posts from Logi1974
- English -
The “Old Cruise” of the Dortmund-Ems Canal near Olfen

In Olfen the Ruhr area becomes the Münsterland region. Agriculture increases suddenly, there are floodplains and the density of settlements decreases. A tour on a bike or a walk is particularly worthwhile here: Olfen has also undergone an exciting development and experienced very special relics of a decommissioned infrastructure.

There is a closed bypass of one of the most important federal waterways in Germany, the Dortmund-Ems Canal. This is an approximately 226 km long artificial waterway between Dortmund and Papenburg on Ems.

The ceremonial opening took place on August 11, 1899, in the presence of Emperor Wilhelm II., after an extremely short construction period of just seven years. From the beginning, the main goals were to relieve the burden on the railways and simplify the transportation of coal from the Ruhr area.

The canal that runs to the North Sea should only be the first step for an entire waterway network. As a connection to the Elbe river, the Mittelland Canal, which of course was still called the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal at that time, was built a few years later.

The Dortmund-Ems Canal originally ran on the section between the Datteln Canal Cross with the nearby Henrichenburg boat lift and Münster city. Directly past the center of Olfen, where there was even a small port. However, the construction of a bypass around Olfen began as early as 1929.

The reason for this was the growing shipping traffic and, of course, new & larger dimensions of the ships. While the canal could simply be dredged wider elsewhere, it wasn´t so easy in Olfen, where the canal ran high above the surrounding country.

Since 1937 the canal has been running on a straightened and widened line southeast of the city. This is called New Cruise or Second Cruise, it´s the oldest of these kind on the Dortmund-Ems Canal. In the further course of the canal, there are a few more bypasses.

With the new cruise, the cruise that have now become the old cruise became less important. In the 1980s, partly because of the high cost of maintenance, it was decided to dismantle this section, with part of the canal and in particular the landscape bridges of Lippe river and Stever river remaining at the canal.

The canal character from the Datteln Sea towards Olfen is still preserved. In sections separated by transverse dams, a long biotope has emerged with a reduced water level, which ends at the former city port of Olfen. The canal is filled up in the city center.

Only at the northern end, where he meets the second cruise, has a marina been built on the old canal route. In the town center, it became an elongated green area on a high causeway with a tree trail. Today the cycle route "Dortmund-Ems Canal", the tour “around Olfen” and the “Stever floodplain trail” run on it.

The preserved Art Nouveau canal bridges from the Emperor period are architecturally impressive. The material is made of sandstone and cast-iron railings are installed in compatible style.
Neandertal valley: Sculpture trail "Human traces"
- English -
The artistic trail Human traces is a sculpture trail in the Neander valley, starting at the Neanderthal Museum, which ten internationally renowned artists have designed.

The sculptures demand a self-reflection and own view of nature. The works are located on a 1.5 km long circular route, along the stream Düssel, from the Neanderthal Museum to the ice age game reserve and back on the other side of the Düssel.

Many of the works have to be actively discovered. An audio guide to the sculpture trail is available at the cash desk of the Neanderthal Museum. The flora is also well worth seeing. In addition to a diverse mixed forest, there are numerous wildflowers to admire.

Immediately to the left of the museum is the work that visitors immediately recognize at the start of the circular route. A series of growing Neanderthal silhouettes cut out of steel plates, seemingly to follow one after the other.

Ben-David used a famous popular scientific drawing of the Neanderthal man from a 1930s Time Life magazine as a template and cut it into industrial steel plates.

Now the sculpture path crosses the busy street. Right behind the Neanderthal kiosk, Volker Friedrich Marten, at the confluence of the Düssel and Mettmanner stream, created a signpost from a burnt-out oak.

The flowing water as a metaphor for the passing of time and the Neander valley itself give the title WOHER-WOHIN a spatial dimension in addition to the spatial dimension.

In a former quarry overgrown with vegetation, Anne and Patrick Poirier created a picture for the memory of the world. They call their work MEMORIA MUNDI, which, above all, becomes a metaphorical image through two foreign elements, an arrow and a brain.

The Poiriers, who deal with places of collective memory, left the quarry as an archaeological site. The picture is intended to remind us of our cultural roots and their preservation.

Passing the Stone Age workshop building, you first follow the signposted circular route to the Ice Age wildlife enclosure. Established in 1935, only three animal species live on the 23-hectare outdoor area today:

Heck cattle (representative of the extinct aurochs), bison and Konik horses (representative of the also extinct tarpan), which were already part of the Neanderthal hunting prey.

The path itself is easy to walk and is mostly wide. Children are also very happy to find their path a little off the way. The old stone quarrys are particularly suitable for climbing.

The Düssel stream remains a constant companion, which winds closer and further away through the original, almost wild forest. Fallen trees lie to the right and left in the undergrowth. It is pleasantly cool here.

Magdalena Abakanowicz's work stands on a wooden box in a nettle clearing behind the Stone Age workshop building: the sculpture of a four-legged animal. The work is entitled MUTANT.

It does not represent this or that animal, it has neither eyes nor face nor character. The artist created the metaphor for this being from sheet steel.

As a teenager, Jaume Plensa was fascinated by the Neanderthal man and his world, without knowing that there even was a place with this name. In the clearing diagonally opposite the mutant is his aluminum question mark titled SEELE (Soul).

Plensa has created an abstract symbol of our written communication system as a sculpture. For Plensa, the question of the soul is the question of the "last things", the nature of human.

The work BEING in the Düssel stream comes from Antony Gormley and is probably often overlooked by visitors. For the Neander valley he created an original cast iron cast of his own body, which, however, does not stand upright like a traditional sculpture, but was laid flat in the course of the Düssel stream.

With a little luck, today's viewer will discover the sculpture when the water level in the Düssel stream is low or the water is clear. Against the background of the Neander valley as a prehistoric site, the sculpture also appears as an archaeological find of the future.

If the visitors walk back to the museum on the other side of the Düssel stream, they encounter an enormous limestone block on the side of the path, which looks like a natural stone from a distance.

If you step closer, you can see that the block has actually been edited. Klaus Simon created a document of human traces of processing from the limestone. If the visitor continues, he will walk over the molded bronze spiral, which is embedded in the path.

Giuseppe Pennone has taken the project "Human traces" at its word. For one quarry on the Düssel stream, Penone designed a hedge from the hornbeam that occurs naturally here, the Neander valley hedge.

Unfortunately, the lighting conditions at this chosen place are so unfavorable that the hedge only grows poorly despite multiple plantings.

The bench on the edge of the path above the former ford through the Düssel stream is also a sculpture. As such, this small, humble work of art by Finlay can easily be overlooked. In his Bugatti Bench the verse is engraved "BARE STREAM RACING LIKE A BUGATTI".

Attentive viewers may be irritated by this strange inscription. Finlay occupies places with words that are often chiseled into simple objects. The viewer receives a quasi-literary instruction manual for the respective location from Finlay.

Unexpectedly, a sign appears under a protective horse chestnut that indicates a work that, however, no longer exists. A large basket weave, similar to a weaver's bird's nest, hung there under the curved branches.

Wickerwork and chestnut have entered into a symbiosis at this place. The artist Nils-Udo called the five-meter-long work HABITAT. Nils-Udo develops shapes that look natural at first glance.

As the path continues, the attentive hiker will come across small surprises. If the children still have energy after all these discoveries, they can let off steam in a large playground on the banks of the Düssel stream.

The sculpture path is free to discover and experience 24/7.
Witten: The Nachtigall colliery (Zeche Nachtigall)
- English -
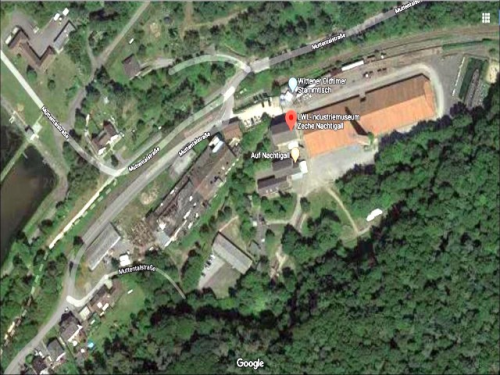
The Nachtigall colliery is located directly on the river Ruhr in Witten. The museum is part of the Westphalian Industrial Museums and shows 300 years of industrial history. The pioneering era of mining comes to life at the Nachtigall colliery in the Witten Ruhr valley.
The location is ideal: right next door is the mine and field railway museum on the former Theresia colliery and on the other hand the very scenic Muttental opens up. As is well known, this was the cradle of Ruhr mining and many remains still testify to this time. This epoch comes to life again on a remarkable tour of mining history.

The farmers in this area had been digging for coal for their own use for centuries. The Nachtigall colliery was founded in 1714. This year, two farmers were given the right to mine coal in the Coal Bank in Hettberger forrest. For a long time, the coal mining was limited to digging holes, the so-called ping. However, damage to the land by ping extracting partially affected agriculture considerably.

In 1743, about 29 years later, the Baron von Elverfeldt acquired the right to mine hard coal for the Nachtigall colliery. The coal was mined in small businesses with three to six men. In the middle of the 18th century, the first tunnel was built.

Water entering the tunnels was discharged through stollen to the river Ruhr. In addition to the water supply, such stollen also discharge the mine gases, supply fresh air and sometimes also transport coal.

The miners often keep goats and pigs for self-sufficiency and grow vegetables, potatoes and fruit. Plums in particular are dried into dried fruit, which often gives workers the name "Prumenkötter".

Since then, the coal mine has been called "Nachtigall am Hettberg". Winders had been used for a long time to extract coal. The drive is initially provided by humans and horses.
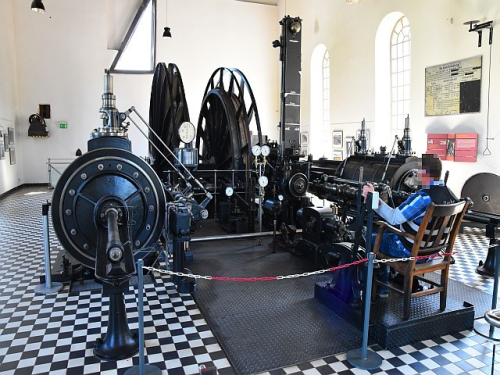
At the turn to the 19th centuries, the transition from tunneling to civil engineering was made at the Nachtigall mine with the help of steam engines. This was only possible through a merger of the mine owners, who could raised the capital for the changeover in this way.

The Nachtigall colliery was one of the first to move from tunnel construction to civil engineering. In 1829 a 6 km long railway for coal transport with horse drive was built. It leads to the coal deposition, south of the road to Wuppertal and the Bergisches Land as well as the Siegerland, to supply the ironworks.

To the north, the Muttental railway leads to the coal deposition on the river Ruhr. As early as 1780, the Ruhr area was navigable from Herdecke to the Rhine - a great relief for coal transportation, which had previously been carried out over long distances with wheelbarrows and horses.

Steam engines soon solved the water drainage problem. They also make it possible to mine coal below the water level of the river Ruhr. In 1832 the first underground shaft of the Nachtigall mine was sunk.

In order to be able to raise the huge amounts of capital required for this, several small mines in the area of Nachtigall come together and establish a company. In 1844, the Nachtigall colliery was the largest in the Ruhr area. In the middle of the 19th century, around 300 to 500 people worked here at depths of up to 450 meters.

A bridge over the river Ruhr, the Nachtigall Bridge, connects the Nachtigall colliery to the Witten-West train station. The connection lies on the Bergisch-Märkische Railway, which opened in 1848.

Coal transport is further facilitated as a railway line runs through the Ruhr Valley from 1874. A separate freight station will soon ensure smooth transportation to and from the coal mine.

In 1890, around 880 miners worked at the Nachtigall colliery. In order to keep the coal price stable and to avoid overproduction, the production volume for the individual mines in the Ruhr area is quoted.

The larger collieries north of the river Ruhr buy up the almost unprofitable collieries in the Muttental in order to be able to mine larger quantities overall. In addition, the coal in the Witten area, unlike the fat coal in the northern areas, is not suitable for coking. In some seams, the supply is also exhausted.

In 1892, the operation of the Nachtigall colliery was stopped after a major water ingress. Most of the miners were housed in the mines of the northern mining region or in other industrial companies. The cessation of mining operations and water management on the colliery is followed by the flooding of the civil engineering mine. However, some pits and tunnels remain water-free, which will be important later on.

The site was then taken over by the entrepreneur Wilhelm Dünkelberg. Dünkelberg had ring ovens built for a steam brick factory above the mine shaft. Brick production on the nightingale began in 1897 as a successor to the mining operation.

She used a dry tunnel through the mountain for the direct transport of raw materials from the quarry to the brick kiln, in this case a double ring kiln with the noticeable and distinctive chimney. The brick press designed by Dünkelberg becomes an export hit - it is sold as far as China.

The brickworks on the grounds of the Nachtigall colliery closed in 1963. A car recycling company and a wreath binder moved in - but only for a short time. The buildings are decaying more and more, the colliery houses are demolished in 1966. In the 1970s, the past was remembered and awareness of the importance of industrial culture began to develop.

In 1983 the landscape association Westfalen-Lippe took over the Nachtigall colliery to the Westphalian Industrial Museum (WIM). Since then, the Nachtigall mine has been restored for over 20 years and officially opened in 2003.

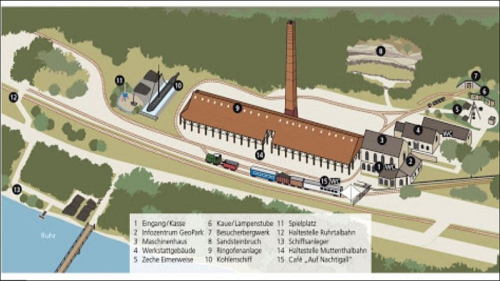
Today the visitor experiences the industrial and traffic history of the Ruhr area. The partially accessible double ring kiln of the former brick factory is particularly impressive. Here you almost feel reminded of old castles and medieval fortifications. A coal ship has moored in the grounds, outside on the premises. Coal used to be transported across the river Ruhr on these sailing ships.

In the exhibition around the filled up “Hercules” shaft from 1839 - one of the first underground shafts in the district - guests learn about the technology and difficult working conditions of the miners in the 19th century.

For many, the absolute highlight of their visit is a visit to the old mine. Like the miners of that time, visitors can explore the tunnel with a helmet, a miner's jacket and a lamp. Former miners tell of the harsh conditions under which the miners once brought the "black gold" to light.

Interested people get to know the work with compressed air drill and mining hammer during the mining trip and can get their own impression of how things are going inside a coal mine.

You can find out about the mining history of the Ruhr Valley in the three surviving factory buildings of the colliery. The main focus is on the origin of coal, the industrial development of the Ruhr Valley, coal consumption, Ruhr shipping and the description of the miner´s job about 150 years ago. A steam Winding engine that has been preserved can even be inspected in operation.

Behind the machine house is the outdoor area with the exhibition "Coal in buckets". A tripod was set up here, which used to be used to extract the coal in buckets from the shaft and load it directly onto carts or wagons.

A primitive booth protects the associated reel system. The facility is surrounded by various small huts with coe and lamp room. There is a quarry at the southern end of the site.

The visitor can inspect the clearly, but lovingly designed area . Most of the exhibits are in closed rooms, which is why a visit in rainy weather is also not a problem. A small café is attached to the museum.

Opening hours Tuesday – Sunday and public holidays 10 am–6pm Last entry at 5:30 p.m.
Closed: Mondays (except public holidays) and from December 23 to January 1.

Entrance fees
Free admission for everyone on the “Museum Days” Children, adolescents and school pupils are free all year round
Adults 4.00 €uros Groups of 16 people or more 3.50 €uros / pp Reduced 2.00 €uros

The entrance prices apply without visit the mining tunnel. Including tunnel admission, the price per ticket increases by 3 €uros, children from 5 years of age pay 1.50 €uros for the tunnel tour.
- English -
Herten Castle
The Herten moated castle is not far from the city center of Herten, what was once the largest mining town on the European continent.

This gem from the Middle Ages lies in the middle of the Ruhr area, in the middle of a large and remarkable castle park with ancient forest. The late Gothic castle and the extensive 30 hectare castle park invite you to visit with the whole family.

Herten Castle was first mentioned in 1376. The family of those von Herten, liege men of the Abbey Werden, was first mentioned in 1286 with Gerlach von Hertene. Their former residence is believed to be in the town center of Herten at the parish church of St. Antonius.

In the 14th century, the knightly family built a permanent house on the site of today's castle, which was mentioned in 1376 as a fief of the Imperial Abbey in Werden. Herten Castle was initially built as a small weir system. The remains of a keep can still be seen today. In the period that followed, expansion and conversion into a representative castle took place.

By marriage, the Herten house came to the Lords of Galen in the mid-14th century. The heiress Elseke brought it to her husband Dietrich von Stecke in 1488 through her marriage in 1476. Anna von Stecke married Bertram von Nesselrode in 1529, heir to the duchies of Jülich and Berg.

Like numerous members of the Nesselrode family, he was a politically influential nobleman at the time and from 1539 to 1556 he was governor of Cologne in the Vest Recklinghausen. From 1530 he had the castle expanded as a closed fort with corner pavilion towers. The towers are still standing today.

The estate remained in the possession of the von Nesselrode family for almost 300 years. After eventful years, a siege in 1593 and a fire almost a century later (1687), Herten Castle was rebuilt by Baron Franz von Nesselrode until 1702. Baron Franz von Nesselrode-Reichenstein was elevated to the status of imperial count by Emperor Leopold I in 1702.

When the last male representative of the von Nesselrode, Johann Franz Josef von Nesselrode, died in 1826, the castle came through Johann's daughter Charlotte to the von Droste zu Vischering family, who was also elevated to the status of an imperial count in the same year.

The members of their Herten lineage then called themselves Droste zu Vischering von Nesselrode-Reichenstein. The family lived at the Herten estate until shortly after the First World War. However, after they moved to Merten Castle in Eitorf from 1920 and thus gave up Herten Castle as a place of residence, it was left to decay.

The castle remained unused and fell visibly into disrepair until it was sold to the Landscapes Association of Westphalia-Lippe in 1974. The site was renovated until 1989, making it accessible to the public.

The State clinic for psychiatry and psychotherapy Herten is located in the western part, which also uses some historical buildings of the castle. The main castle is reached via a bridge from the outer castle, which in turn is surrounded by a moat and contains a coach house and chapel.

The main castle is today a late Gothic brick building with a closed courtyard. The four parts of the building surrounding it have the shape of a trapezoid. The castle with its characteristic corner towers is surrounded by a moat, a moat. The castle is partially accessible, for example, offers a restaurant, but is mainly used by the clinic.

After the Schlosspark was awakened from its more than 50-year-old sleeping beauty in 1974, as a People's park it is an integral part of the life of (not only) the people of Herten.

Between 1687 and 1702 the park was transformed from a strict baroque garden into a landscape park based on the English model. Count von Nesselrode even engaged Düsseldorf court gardener Maximilian Friedrich Weyhe to design the palace park.

The small pavilion, Tobacco house, in the castle park got its name from the two Counts Riaucourt - sons of a countess Nesselrode - who found shelter in Herten Castle from the French Revolution. In this garden shed they enjoyed the new fashion of smoking in front of the fireplace, which was frowned upon in the castle.

The orangery, built in 1725, was decorated by a balustrade with 12 statues at the time. It housed the garden casino, court parties were celebrated, orange and ornamental trees were raised and there was space for one of the most beautiful camellia collections.

In the meantime there is unfortunately only a ruin left. Missing repairs and mining damage hit the building, which was only partially renovated in the 1970s. The reconstruction of the surprisingly large orangery is still under discussion.

After the noble family moved from Nesselrode to Merten Castle in 1920, the park was only opened for special celebrations and processions. For nature and animals, it was a relaxing time behind the walls. The park overgrown, but also the Herten moated castle and the orangery decayed over time.

When the Land Association of Westphalia-Lippe bought the property with the castle in 1974, considerable renovation measures were necessary. Between 1974 and 1976 over 2 million DM were invested in the castle park alone. It was only made accessible when it was acquired by the state association.

Botanical treasures from all over the world can be found in the Herten castle park - chile fir trees, Japanese cypresses, katsura trees or catalpa and ghost trees. The star magnolia in front of the castle is one of the oldest in Westphalia.

The park was structured in a varied way with meadows, avenues, squares or even a rose garden and invites you to stroll. Rare giant trees, old forests, daffodil meadows, the maze and the open-air theater are grouped around the Herten Castle.

The castle ponds adjoin the picturesque moats, which are particularly impressive due to their biodiversity of waterfowl. Unfortunately, tons of invasive geese (Egyptian geese and Canada geese) have settled here, which obviously feel very comfortable and reproduce splendidly.

The green areas are correspondingly contaminated and the ponds are also badly affected by this overpopulation.

Entry to the castle park is possible 24/7 and free of charge!
Mettmann: Excavation site of the Neanderthal man
- English -
The Mettmann district is world famous - even if hardly anyone in Africa or America knows the name of the region.
However, the name of the most prominent inhabitant is on everyone's lips: in 1856 the remains of the Neanderthals were found here. The district of Mettmann is the first place of discovery of a Neanderthal man worldwide.

The Neanderthals lived in Europe for 250,000 years, adapted to the harsh living conditions of the Ice Age. The discovery of their remains revealed that they actually existed: 40,000 years before our era, a group of people trudged across the plateau near the stream Düssel.

Her forehead is flat, her eye brows are with thick bulged. They wear furs on their bodies as protection against the icy wind. Their feet wander over stones and hard frozen earth. The ice age has Europe under control.

Since there were only a few edible plants in the cool environment, the small tribal groups probably walked behind the grazing animal herds of the Ice Age.

A cave has been washed out of the limestone cliffs of the stone plateau by the stream Düssel and smaller tributaries in millions of years. One of these early humans was buried in this cave about 20 meters above the Düssel. His 16 surviving bones can be seen today in the Neanderthal Museum.

The researchers owe the discovery of the skeleton to limestone mining, which began in the course of industrialization in the 19th century. Even today, the walls in the Neandertal occasionally shake when an explosion is carried out in the last remaining limestone factory.

Limestone became a coveted raw material in the middle of the 19th century. It is required for steel production in the iron industry and as a building material. In 1849, mining began on a large scale in the Neandertal.

The region owes its name to the theologian and hymn writer Joachim Neander, who held services in the 17th century in the then narrow and deep gorge and composed hymns. The Neandertal has long been known to connoisseurs for its rich diluvial deposits.

While working, miners encountered the skeletal parts in the cave. This cave was 3 m wide, 5 m long and 3 m high. The workers cleared the grotto and initially paid little attention to the bones found, because bones from extinct animals were found here very often.

For the workers, the bones looked like those of cave bears, so they threw them away. On the bones you can still clearly see the damage that the workers inflicted on the Neanderthal man with pickaxes.

The clearly visible chipping marks show that the bones were in the anatomical bandage. The left half of the hip and the joint head of the thigh were damaged when exposed. The remaining furrow flows smoothly from one bone to the other.

The fossil finds happened to be noticed by the co-owner of the Neanderthal quarry, Wilhelm Beckershoff, who was just there. His business partner Friedrich Wilhelm Pieper handed them over to the locally known natural scientist Dr. Johann Carl Fuhlrott. Fuhlrott looked at the pieces and quickly noticed that this skeleton had to belong to a diluvial prehistoric man.

Between 1997 and 2000, Ralf Schmitz and Jürgen Thissen carried out additional excavations in the Neandertal, in which 62 further bone fragments were found. Among them were six moreNeanderthal teeth, these may have belonged to the find from 1856.

Some bone fragments matched the 1856 skeleton. There have been so many bones since the excavation that at least one other adult and one sub-adult Neanderthal man is assumed.

The valley is no longer narrow and deep and the waterfalls, cliffs and magnificent caves have largely disappeared. Progress is more important than nature. When the area was placed under nature protection in 1921, the steep gorge had already became a wide, treeless valley.

Millions of tons of rock have been removed in the course of industrialization. The Feldhofer grottoes and Joachim Neander's favorite place no longer exist. Nothing reminds of the Neanderthal's habitat.

The explosions completely destroyed the picturesque rock canyon. For this, beech, hornbeam and canyon forests have conquered the region, which cover the hills and slopes and immerse the former quarries in lush green.

Landscape architects have staged the site as an archaeological garden that tells the eventful history of the valley. If you like, you can also have all of the points from the excavation site explained by an audio system.

There are now a few stone loungers at the site. And a few poles are set up. But the place is really informative thanks to the numerous information from the app or via headphones, for which there are numerous opportunities to plug in.

A lot of information can be heard on headphones, which you can borrow for the tour. If you want to hear all of this on your cell phone, you have been able to download a Neanderthal Museum app for some time now, which has exciting information on all points.

We were positively surprised by the numerous facts that are prepared in such a playful way. If you are traveling in the region, you should definitely stop by there. Warning: the excavation site closes earlier than the museum.

The Neanderthal Museum, opened in 1996, offers further information. The striking spiral building is only a few hundred meters from the site. A paved path leads as a timeline to the place of the historical site.

No admission was charged at the site during our visit!