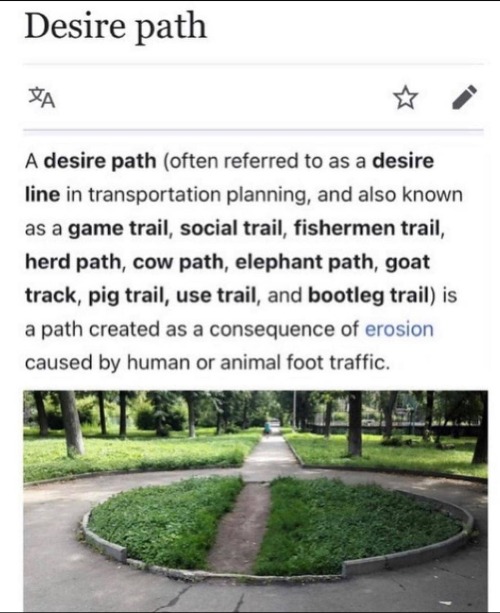
Urban Planning - Tumblr Posts

As relentless rains pounded LA, the city’s “sponge” infrastructure helped gather 8.6 billion gallons of water—enough to sustain over 100,000 households for a year.
Earlier this month, the future fell on Los Angeles. A long band of moisture in the sky, known as an atmospheric river, dumped 9 inches of rain on the city over three days—over half of what the city typically gets in a year. It’s the kind of extreme rainfall that’ll get ever more extreme as the planet warms.
The city’s water managers, though, were ready and waiting. Like other urban areas around the world, in recent years LA has been transforming into a “sponge city,” replacing impermeable surfaces, like concrete, with permeable ones, like dirt and plants. It has also built out “spreading grounds,” where water accumulates and soaks into the earth.
With traditional dams and all that newfangled spongy infrastructure, between February 4 and 7 the metropolis captured 8.6 billion gallons of stormwater, enough to provide water to 106,000 households for a year. For the rainy season in total, LA has accumulated 14.7 billion gallons.
Long reliant on snowmelt and river water piped in from afar, LA is on a quest to produce as much water as it can locally. “There's going to be a lot more rain and a lot less snow, which is going to alter the way we capture snowmelt and the aqueduct water,” says Art Castro, manager of watershed management at the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. “Dams and spreading grounds are the workhorses of local stormwater capture for either flood protection or water supply.”
Centuries of urban-planning dogma dictates using gutters, sewers, and other infrastructure to funnel rainwater out of a metropolis as quickly as possible to prevent flooding. Given the increasingly catastrophic urban flooding seen around the world, though, that clearly isn’t working anymore, so now planners are finding clever ways to capture stormwater, treating it as an asset instead of a liability. “The problem of urban hydrology is caused by a thousand small cuts,” says Michael Kiparsky, director of the Wheeler Water Institute at UC Berkeley. “No one driveway or roof in and of itself causes massive alteration of the hydrologic cycle. But combine millions of them in one area and it does. Maybe we can solve that problem with a thousand Band-Aids.”
Or in this case, sponges. The trick to making a city more absorbent is to add more gardens and other green spaces that allow water to percolate into underlying aquifers—porous subterranean materials that can hold water—which a city can then draw from in times of need. Engineers are also greening up medians and roadside areas to soak up the water that’d normally rush off streets, into sewers, and eventually out to sea...
To exploit all that free water falling from the sky, the LADWP has carved out big patches of brown in the concrete jungle. Stormwater is piped into these spreading grounds and accumulates in dirt basins. That allows it to slowly soak into the underlying aquifer, which acts as a sort of natural underground tank that can hold 28 billion gallons of water.
During a storm, the city is also gathering water in dams, some of which it diverts into the spreading grounds. “After the storm comes by, and it's a bright sunny day, you’ll still see water being released into a channel and diverted into the spreading grounds,” says Castro. That way, water moves from a reservoir where it’s exposed to sunlight and evaporation, into an aquifer where it’s banked safely underground.
On a smaller scale, LADWP has been experimenting with turning parks into mini spreading grounds, diverting stormwater there to soak into subterranean cisterns or chambers. It’s also deploying green spaces along roadways, which have the additional benefit of mitigating flooding in a neighborhood: The less concrete and the more dirt and plants, the more the built environment can soak up stormwater like the actual environment naturally does.
As an added benefit, deploying more of these green spaces, along with urban gardens, improves the mental health of residents. Plants here also “sweat,” cooling the area and beating back the urban heat island effect—the tendency for concrete to absorb solar energy and slowly release it at night. By reducing summer temperatures, you improve the physical health of residents. “The more trees, the more shade, the less heat island effect,” says Castro. “Sometimes when it’s 90 degrees in the middle of summer, it could get up to 110 underneath a bus stop.”
LA’s far from alone in going spongy. Pittsburgh is also deploying more rain gardens, and where they absolutely must have a hard surface—sidewalks, parking lots, etc.—they’re using special concrete bricks that allow water to seep through. And a growing number of municipalities are scrutinizing properties and charging owners fees if they have excessive impermeable surfaces like pavement, thus incentivizing the switch to permeable surfaces like plots of native plants or urban gardens for producing more food locally.
So the old way of stormwater management isn’t just increasingly dangerous and ineffective as the planet warms and storms get more intense—it stands in the way of a more beautiful, less sweltering, more sustainable urban landscape. LA, of all places, is showing the world there’s a better way.
-via Wired, February 19, 2024
Homesteading for the Homeless:
How Converting Empty Commercial Spaces into Indoor Farms Can Address Food Insecurity and Unemployment
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to high vacancy rates for commercial spaces in metropolitan areas, especially malls and skyscrapers. At the same time, homelessness remains a significant issue, especially in coastal cities. One solution to address both these problems is to convert empty commercial spaces into indoor farms and communal living areas for homeless Americans, owned and operated by their workers.
Indoor farming has emerged as a sustainable and efficient method for producing high yields of crops in a small space, regardless of weather or climate conditions. Vertical farming, a method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, has gained popularity in recent years as a way to maximize space and improve efficiency. Repurposing vacant commercial buildings could create a new industry that addresses food insecurity while providing employment for the homeless.
According to a report from CBRE, the United States had a 16.4% office space vacancy rate at the end of 2020, the highest it has been since 2011. The retail sector was also struggling, with a national vacancy rate of 10.5% in the first quarter of 2021. Meanwhile, homelessness remains a significant issue in coastal cities, with an estimated 580,466 people experiencing homelessness in January 2020, according to the Department of Housing and Urban Development.
Startups in the vertical farming industry have been on the rise in recent years. According to AgFunder, an online platform that connects investors with agtech startups, there were over 60 vertical farming startups that raised over $1.2 billion in funding in 2020. These startups are using innovative techniques to grow crops in urban areas, close to consumers, and reduce transportation costs and emissions.
Converting vacant commercial buildings into indoor farms using vertical farming techniques would provide employment for the homeless and communal living spaces. However, these indoor farms could also be operated as worker-owned commercial enterprises. Communal living spaces for homeless individuals would provide a sense of community and stability, as well as a chance to learn valuable skills through participation in the farming process. By operating the indoor farms as worker-owned enterprises, homeless individuals could take ownership of their work and have a say in the direction of the business.
Homesteading using vertical farming is an opportunity to work with individuals who share the same interests and values. For young people, WWOOF (World Wide Opportunities on Organic Farms) provides opportunities to travel around the world and learn about sustainable agriculture practices. Similarly, converting commercial spaces into worker-owned indoor farms could create new opportunities for homeless individuals to participate in the farming process and learn valuable skills, while also taking ownership of their work.
While there are challenges to converting commercial buildings into worker-owned indoor farms, such as significant investment and expertise, the benefits are significant for those experiencing homelessness and the wider community. By creating worker-owned indoor farms, we could create a new industry that provides stability, food security, and employment opportunities, while building a stronger sense of community.
The conversion of vacant commercial buildings into worker-owned indoor farms using vertical farming techniques and communal living spaces for the homeless could address the challenges facing our society. We have the potential to create a new industry that provides stability, food security, and employment opportunities, while building a stronger sense of community. Let us consider homesteading with worker-owned indoor farming as a solution for the future.
it’s always amazing to watch adults discover how much changes when they don’t treat their perspective as the default human experience.
example: it’s been well-documented for a long time that urban spaces are more dangerous for kids than they are for adults. but common wisdom has generally held that that’s just the way things are because kids are inherently vulnerable. and because policymakers keep operating under the assumption that there’s nothing that can be done about kids being less safe in cities because that’s just how kids are, the danger they face in public spaces like streets and parks has been used as an excuse for marginalizing and regulating them out of those spaces.
(by the same people who then complain about kids being inside playing video games, I’d imagine.)
thing is, there’s no real evidence to suggest that kids are inescapably less safe in urban spaces. the causality goes the other way: urban spaces are safer for adults because they are designed for adults, by adults, with an adult perspective and experience in mind.
the city of Oslo, Norway recently started a campaign to take a new perspective on urban planning. quite literally a new perspective: they started looking at the city from 95 centimeters off the ground - the height of the average three-year-old. one of the first things they found was that, from that height, there were a lot of hedges blocking the view of roads from sidewalks. in other words, adults could see traffic, but kids couldn’t.
pop quiz: what does not being able to see a car coming do to the safety of pedestrians? the city of Oslo was literally designed to make it more dangerous for kids to cross the street. and no one realized it until they took the laughably small but simultaneously really significant step of…lowering their eye level by a couple of feet.
so Oslo started trimming all its decorative roadside vegetation down. and what was the first result they saw? kids in Oslo are walking to school more, because it’s safer to do it now. and that, as it turns out, reduces traffic around schools, making it even safer to walk to school.
so yeah. this is the kind of important real-life impact all that silly social justice nonsense of recognizing adultism as a massive structural problem can have. stop ignoring 1/3 of the population when you’re deciding what the world should look like and the world gets better a little bit at a time.
Why can’t we have nice things here?

"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
250 people per train car sounds inaccurate (that’s how many people can fit to light rail 2 car trains in my area), but 66/67 people on the bus sounds reasonable.
„my averege bus” can hold up to 80-90 people - unarticulated city bus with about 20-30 sitting places.
If you count articulated buses - you can fit 140 people in them (40 sitting places)

@ 2:36 in their video title We Might Be Able to Fix the Suburbs, StreetCraft says "roundabouts have been proven to reduce the risk of a fatal crash by 90%, and if this was the design from the start, these two teenagers could've graduated from high school." and that just hit me real hard
I forget sometimes that like traffic engineering is indeed very valid, and I forget that there are people out there who surely must know that in their life-or-death urban planning decisions they are straight up in favour of death if it means slightly faster shipping times
https://youtu.be/nQKCYxYCluA?si=iB39VaBAAFfIhmhf
Goes to show that we need something to balance out the allergens in a city with something, even if it means a bit of mess trade-off. Maybe we can spread the seeds that fall into untapped spots to allow for a further cultivation upon the cityscapes for a better distribution. My editor would be more than happy to encourage a better balancing for these for us and the trees.

Botanical Sexism Cultivates Home-Grown Allergies
Arborists often claim that all-male plants are “litter-free” because they shed no messy seeds, fruits or pods. In the 1949 USDA Yearbook of Agriculture, which focused on trees and forests, this advice was given to readers: “When used for street plantings, only male trees should be selected, to avoid the nuisance from the seed.” In the years following, the USDA produced and released into the market almost 100 new red maple and hybrid-maple-named clones (cultivars), and every single one of them was male.
It took a number of years for these new trees to mature enough to start to bloom, but eventually they did and with them came more city pollen and the “epidemic of allergy and asthma.” Many of these same trees are still alive and well and getting even larger, and the bigger they get, the more pollen they shed.
Allergies are rarely triggered by small amounts of an allergen; they are initiated by an overdose. Small amounts of pollen exposure are actually good for us, but if we have highly allergenic trees or shrubs in our own yards or lining our streets, we will soon enough be over-exposed. In order to put the brakes on America’s allergy epidemic, we need to reverse the trend toward male-dominated landscapes and stop selling and planting any more of the most allergenic trees, shrubs and grasses in our cities.
and the kicker:
Female trees produce no pollen, but they trap and remove large amounts of pollen from the air, and turn it into seed. Female trees (and female shrubs also) are not just passive, but are active allergy-fighting trees. The more female plants in a landscape, the less pollen there will be in the air in the immediate vicinity. By relying less on males and paying more attention to the allergy-potential of all the plants in our urban landscape, all of us may one day breathe easier.
We’ll have to rip up the current version of urban planning. More walkable cities and neighborhoods. Less suburban sprawl. God please let this happen
Here’s a radical idea.
Let’s not only build more public parks, let’s build more public parks and install as much native vegetation as possible? More water efficient, more public space where you can hang out with your friends without being accused of loitering, better for the environment, and an accessible place for people to still be near nature.

Almost Upscale: Columbia Heights wants to build America’s first city hall in a luxury apartment building
City Pages
Very important. Personally I think we should just straight up ban personal cars in cities.