Biblical Criticism - Tumblr Posts
The Bible's Tenses Are in a Timeless Context: God "Declaring The End from The Beginning" (Isaiah 46:10)
Goodreads Author Eli kittim
"The Lamb that was slain from the creation of the world." (Rev. 13:8). Was Jesus slain before the world was even made?
"Children it is the last hour; ... even NOW many antichrists have arisen; from this we know that IT IS THE LAST HOUR." (1 John 2:18). Is John implying that 95 AD is the end of the world?
"In THESE LAST DAYS [God] has spoken to us in His Son." (Heb. 1:2). Is the author suggesting that the last days of the world happened during his life time?
"He [Jesus] … WAS revealed at the final point of time” (1 Pet. 1:20, New Jerusalem Bible, ). Is the final point of time in the past?
In the book of Revelation, in reference to a future event, John writes: “From the tribe of Judah, twelve thousand HAD BEEN sealed” (Rev. 7:5, New Jerusalem Bible). Is the future in the past? Surely, "had been" is past tense!
Thus, the Bible is written in a timeless context as though everything is happening now! It's speaking to all generations and to all periods of history. It isn't writing exclusively about past history as most people mistakenly believe!
The Little Book of Revelation: The First Coming of Jesus at the End of Days - Kindle edition by Eli of Kittim. Download it once and read it on your Kindle device, PC, phones or tablets. Use features like bookmarks, note taking and highlighting while reading The Little Book of Revelation: The First Coming of Jesus at the End of Days.
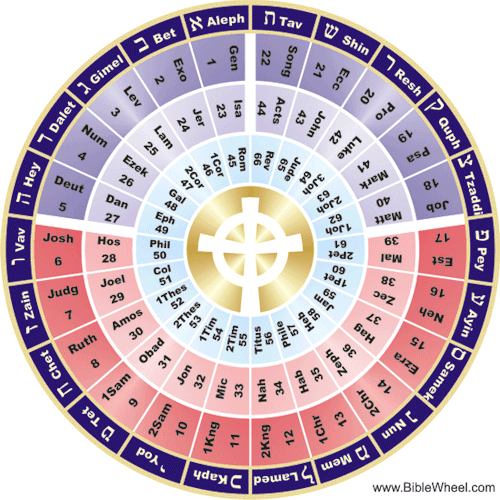
A Critical Review of the So-Called “Bible-Wheel” method of Biblical Interpretation
By Author Eli Kittim
——-
Like the Zohar in the Kabbalah, the “Bible-Wheel” approach is a kind of Hebraic “Gematria” or “Isopsephy” that corresponds to the letters of the Hebrew alphabet but does not take into consideration several important Biblical factors. For instance, it doesn’t consider the fact that the New Testament uses a different alphabet (i.e. Greek), nor does it seriously consider the historical-grammatical context of the New Testament books. The Bible Wheel’s premise is that “the Hebrew alphabet is established in the alphabetically structured passages of the Old Testament, most notably Psalm 119 that praises God's Word from Aleph to Tav, from beginning to end.” This “is a circular presentation of the Bible . . . by rolling up the traditional list of the sixty-six books like a scroll on a spindle wheel of twenty-two spokes.” Here’s how it works:
“The structure consists of a circular matrix of sixty-six Cells on a Wheel of twenty-two Spokes. The sixty-six Cells form three wheels within the Wheel called Cycles. Each Cycle spans a continuous sequence of twenty-two books as follows: With the completion of the Bible Wheel, we now have a fully unified view of the whole Bible as a symmetrical, mathematically structured two-dimensional object. The increase from the traditional one-dimensional list of books to the two-dimensional Bible Wheel immediately reveals a host of unanticipated correlations between the three books on each spoke with each other and the corresponding Hebrew Letter” (according to biblewheel.com).
This is more of an “intuitive” rather than a scholarly approach to the Bible that is devoid of historical, grammatical, hermeneutical, and contextual considerations. For example, the premise that the entire Biblical structure of the 66 canonical books is grounded exclusively in the Hebrew alphabet “from Aleph to Tav, from beginning to end” is debunked by Christ’s self-disclosure and promulgation of the Divine Name explicitly through the Greek alphabet:
ἐγὼ τὸ Ἄλφα καὶ τὸ Ὦ, ὁ πρῶτος καὶ ὁ ἔσχατος, ἡ ἀρχὴ καὶ τὸ τέλος (SBLGNT).
Translation:
“I am the Alpha and the Omega, the First and the Last, the Beginning and the End” (Rev. 22.13 NRSV).
There is absolutely no correlation, here, to the Aleph and Tav or to the Hebrew alphabet. On the contrary, Christ reveals the divine name in the language of the Greeks by declaring “I am the Alpha and the Omega, the First and the Last, the Beginning and the End.” The alpha and omega are the first and last letters of the Greek writing system, that is to say, the beginning and the end of the Greek alphabet!
What is more, the Bible wheel practice is based not on scholarly criteria (i.e. detailed exegesis/authorial intent) but rather on apparent coincidences (e.g. mathematical, alphabetic, Hebraic, etc.), sometimes explained through a matrix that we might call “synchronicity”:
//Synchronicity is a concept, first introduced by analytical psychologist Carl Jung, which holds that events are "meaningful coincidences" if they occur with no causal relationship yet seem to be meaningfully related. During his career, Jung furnished several different definitions of the term, defining synchronicity as an "acausal connecting (togetherness) principle;" "meaningful coincidence;" "acausal parallelism;” and as a "meaningful coincidence of two or more events where something other than the probability of chance is involved.// (Wiki).
Therefore, although it may have some symbolic preliminary merits, the Bible wheel practice is obviously not a credible or scholarly approach to Biblical investigation.
The notion that the 66 Books of the Bible can be put on an apparent wheel where each book directly coincides with some other book based on certain numerical, alphabetical, and Hebraic correlations seems to be an outlandish explanation! This practice, including its pictorial representation, is somewhat reminiscent of the medieval divination practices of occultism, such as Kabbalah, Cartomancy (i.e. Tarot card reading) and Numerology:
“Numerology is any belief in the divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value of the letters in words, names, and ideas. It is often associated with the paranormal, alongside astrology and similar divinatory arts” (Wiki).
——-
The idea behind the Bible-Wheel approach is that Biblical history repeats itself: that time is cyclical. What is the axiom of this interpretive method? As It Was, So Shall It Be… It, therefore, presupposes that there are thematic parallels (and secret codes) between the earlier books of the Bible and the later ones. Similar methods have been proposed by authors Perry Stone and Jonathan Cahn. Thus, with the exception of some trivial and peripheral similarities, I don’t see any major thematic affinities, say, between Jeremiah 17 and Revelation 2, as per the Bible-wheel interpretation.
——-
Let’s Look at Rev. 2
——-
The Church of Ephesus has a lot going for it. It endures with patience, does not tolerate evil, exposes falsehood, and bears much for the sake of Christ (Rev. 2.2-3). No such praise is ever mentioned in Jer. 17 in relation to to the Jews. Furthermore, despite some set backs, God promises certain divine rewards in Rev. 2 that are not mentioned in Jer. 17, namely, offering the faithful the crown of life (Rev. 2.10) as well as eternal life: “Whoever conquers will not be harmed by the second death” (Rev. 2.11), etc.
——-
Similarly, the Church of Pergamum, despite its shortcomings, is holding fast. Even though it’s located within Satan’s domain, so to speak, it’s holding on to Christ and has not denied the faith (Rev. 2.13).
Here, as before, Christ offers the divine manna and a mystic precious stone to the over-comers (Rev. 2.17). Nothing of the kind is ever referenced in Jer. 17.
——-
Also, the Church in Thyatira is not doing too bad either. Christ is aware of its works—such as “love, faith, service, and patient endurance” (Rev. 2.19). And although some have incorporated certain false teachings, there are others within the church that are blameless and whom Christ does not rebuke at all (Rev. 2.24)! He simply urges them to hold on til he comes (Rev. 2.25). Christ maintains that anyone who endures to the end will be granted “authority over the nations” (v. 26) and will also receive “the morning star” (v.28).
——-
Now Let’s Look at Jer. 17
——-
By contrast, Jeremiah 17 is casting an aspersion on the kingdom of Judah. Its proemium is as follows:
“The sin of Judah is written with an iron pen; with a diamond point it is engraved on the tablet of their hearts, and on the horns of their altars” (Jer. 17.1 NRSV).
Next, there are a number of caveats that culminate in God’s vow to eternally disinherit the Jews from his promises:
“By your own act you shall lose the heritage that I gave you, and I will make you serve your enemies in a land that you do not know, for in my anger a fire is kindled that shall burn forever” (v. 4). Then God recites a summary of the Blessings and Curses of the covenant (vv. 5-9). Finally, Jeremiah exalts the Lord and offers up his own defense that he is upright, and so on. Here, the text instructs the people of Judah to keep certain commandments, such as “the sabbath day” (v. 24), something that does not occur in Rev. 2. The chapter ends with Blessings and Curses in the form of rewards and punishments (vv. 26-27).
Incidentally, the theme of God who “searches minds and hearts,” in Rev. 2.23, is a common trope that can be found in various places in the Bible and is not exclusive to Jeremiah 17.10 (e.g., 1 Ch. 28.9; 29.17; Ps. 7.9; Prov. 17.3; Ecc. 3.18; Jer. 11.20; Rom. 8.27), as proponents of this view suggest.
——-
Conclusion
Unlike Rev. 2, nowhere is there any mention of eternal life or of surviving a second death in Jer. 17. Moreover, no one is offered any rewards of authority over nations, or any glory, for that matter, such as that implied by the so-called “morning star.” In fact, there’s no one blameless in Jer. 17, nor does any praise come from God concerning anyone whatsoever. Even the prophet himself has to plead for mercy and proclaim his own self-righteousness. Besides, there are so many other differences.
Jeremiah is written in *Hebrew* and heavily redacted probably by the scribe Baruch and later generations of Deuteronomists, while Revelation is written exclusively in *Greek* most likely by a single author. The former is probably from the 6th century BCE, while the latter dates from ca. 95 CE. One is written to a Jewish nation, the kingdom of Judah, just prior to the Babylonian deportation, while the other is written to the predominantly Gentile Churches in Asia Minor. One is written in Palestine, the other in Greece! So where are the parallels?
——-

How Can Good Exegesis Make Bad Theology?
By Author Eli Kittim
——-
The Canonical Context
This principle suggests that we should read the Books of the Bible not as distinct, individual compositions but rather as parts of a larger *canonical context*, that is, as part of the “canon” of Scripture. In other words, instead of evaluating each book separately in terms of its particular historical, literary, and editorial development, this principle focuses instead on its final canonical format that was legitimized by the various communities of faith. The idea is that since the redacted version or “final cut,” as it were, is considered “authoritative” by the different communities of faith, then this format should hold precedence over all previous versions or drafts.
Moreover, this concept holds that despite the fact that the Biblical Books were written by a number of different authors, at different times, in different places, using different languages, nevertheless the “canonical context” emphasizes the need to read these Books in dialogue with one another, as if they are part of a larger whole. So, the hermeneutical focus is not on the historical but rather on the canonical context. The hermeneutical guidelines of the canon therefore suggest that we might gain a better understanding of the larger message of Scripture by reading these Books as if they were interrelated with all the others, rather than as separate, diverse, and distinct sources. The premise is that the use of this type of context leads to sound Biblical theology.
——-
Theology
Theology is primarily concerned with the synthesis of the diverse voices within Scripture in order to grasp the overarching message of the complete Biblical revelation. It deals with Biblical epistemology and belief, either through systematic analysis and development of passages (systematic theology) or through the running themes of the entire Bible (Biblical theology). It addresses eternity and the transcendent, metaphysical or supernatural world. And it balances individual Scriptural interpretations by placing them within a larger theoretical framework. The premise is that there is a broader theological context in which each and every detailed exegesis coalesces to form a coherent whole! It’s as if the Bible is a single Book that contains a complete and wide-ranging revelation! It is under the auspices of theology, then, that the canonical context comes into play.
——-
Exegesis
The critical interpretation of Scriptural texts is known as “exegesis.” Its task is to use various methods of interpretation so as to arrive at a definitive explanation of Scripture! Exegesis provides the temporal, linguistic, grammatical, and syntactic context, analysis, and meaning of a text. It furnishes us with a critical understanding of the authorial intent, but only in relation to the specific and limited context of the particular text in question. It is the task of theology to further assess it in terms of its relation and compatibility to the overall Biblical revelation! One of the things that exegesis tries to establish is the composition’s historical setting or context, also known as “historical criticism.” This approach inquires about the author and his audience, the occasion and dating of the composition, the unique terms and concepts therein, the meaning of the overall message, and, last but not least, the *style* in which the message is written, otherwise known as the “genre.” While the author’s other writings on the topic are pivotal to understanding what he means, nothing is more important than the *genre* or the form in which his writing is presented.
——-
The Analogy of Scripture
One of the most important hermeneutical principles of exegesis is called “the analogy of Scripture” (Lat. ‘analogia Scripturae’). In short, it means that Scripture should interpret Scripture. This principle requires that the implicit must be explained by the explicit. In other words, the exegesis of unclear or ambiguous parts of Scripture must be explained by clear and didactic ones that address the exact same topic. That means that one Biblical Book could very well explain another. For example, the New Testament (NT) Book of Ephesians 1.9-10 seems to demystify Galatians 4.4. This principle is based on the “revealed” inspiration (Gk. θεόπνευστος) of Scripture:
All scripture is inspired by God and is useful
for teaching, for reproof, for correction, and
for training in righteousness (2 Tim. 3.16
NRSV).
As for those scholars who refuse to take the NT’s alleged “pseudepigrapha” seriously because of their *apparent* false attribution, let me remind them that the most renowned textual scholars of the 20th century, Bruce M. Metzger and Bart D. Ehrman, acknowledged that even alleged “forged” works could still be “inspired!” It’s important to realize that just because these works may be written by unknown authors who may have attempted to gain a readership by tacking on the name of famous Biblical characters doesn’t mean that the subject-matter is equally false. The addition of amanuenses (secretaries) further complicates the issue.
So, returning to our subject, the analogy of Scripture allows the Bible to define its own terms, symbols, and phrases. It is via the analogy of Scripture, which defines the many and varied parts, that the broader canonical context is established, namely, the principle that the various Biblical Books form a coherent whole from which a larger theological system can emerge.
And, of course, interdisciplinary studies——such as archaeology, anthropology, psychology, sociology, epistemology, and philosophy——contribute to both systematic and Biblical theology by presenting their particular findings, concepts, and theoretical ideas.
——-
Testing the Legitimacy of these Principles
In explaining how these principles work in tandem, I’d like to put my personal and unique theology to the test. I have raised the following question: “What if the crucifixion of Christ is a future event?” The immediate reaction of Christian apologetics or heresiology would be to revert to “dogmatic theology” (i.e., the dogmas or articles of faith) and the scholarly consensus, which state that Jesus of Nazareth was crucified under Pontius Pilate during the reign of Tiberius. Really? Let’s consider some historical facts. There are no eyewitnesses! And there are no first-hand accounts! Although the following references were once thought to be multiple attestations or proofs of Jesus’ existence, nevertheless both the Tacitus and Josephus accounts are now considered to be either complete or partial forgeries, and therefore do not shed any light on Jesus’ historicity. One of the staunch proponents of the historical Jesus position is the textual scholar Bart Ehrman, who, surprisingly, said this on his blog:
. . . Paul says almost *NOTHING* about the
events of Jesus’ lifetime. That seems weird
to people, but just read all of his letters.,
Paul never mentions Jesus healing anyone,
casting out a demon, doing any other
miracle, arguing with Pharisees or other
leaders, teaching the multitudes, even
speaking a parable, being baptized, being
transfigured, going to Jerusalem, being
arrested, put on trial, found guilty of
blasphemy, appearing before Pontius Pilate
on charges of calling himself the King of the
Jews, being flogged, etc. etc. etc. It’s a
very, very long list of what he doesn’t tell us
about.
Therefore, there appears to be a literary discrepancy regarding the historicity of Jesus in the canonical context between the gospels and the epistles. And, as I will show in due time, there are many, many passages in the epistles that seem to contradict dogmatic theology’s belief in the historiographical nature of the gospels. So, if they want to have a sound theology, exegetes should give equal attention to the epistles. Why?
First, the epistles precede the gospels by several decades. In fact, they comprise the earliest recorded writings of the NT that circulated among the Christian churches (cf. Col. 4.16).
Second, unlike the gospels——which are essentially *theological* narratives that are largely borrowed from the Old Testament (OT)——the epistles are *expositional* writings that offer real, didactic and practical solutions and discuss spiritual principles and applications within an actual, historical, or eschatological context.
Third, according to Biblical scholarship, the gospels are not historiographical accounts or biographies, even though historical places and figures are sometimes mentioned. That is to say, the gospels are not giving us history proper. For example, the feeding of the 5,000 is a narrative that is borrowed from 2 Kings 4.40-44. The parallels and verbal agreements are virtually identical. And this is a typical example of the rest of the narratives. For instance, when Jesus speaks of the damned and says that “their worm never dies, and the fire is never quenched” (Mark 9.48), few people know that this saying is actually derived from Isaiah 66.24. In other words, the gospels demonstrate a literary dependence on the OT that is called, “intertextuality.”
Fourth, the gospels are like watching a Broadway play. They are full of plots, subplots, theatrical devices (e.g. Aristotelian rhetoric; Homeric parallels), literary embellishments, dialogues, characters, and the like. Conversely, the epistles have none of these elements. They are straightforward and matter of fact. That’s why Biblical interpreters are expected to interpret the implicit by the explicit and the narrative by the didactic. In practical terms, the NT epistles——which are the more explicit and didactic portions of Scripture——must clarify the implicit meaning of the gospel literature. As you will see, the epistles are the primary keys to unlocking the actual timeline of Christ’s *one-and-only* visitation!
Fifth, whereas the gospels’ literary genre is mainly •theological•——that is to say, “pseudo-historical”——the genre of the epistolary literature of the NT is chiefly •expositional.• So, the question arises, which of the two genres is giving us the real deal: is it the “theological narrative” or the “expository writing”?
In order to answer this question, we first need to consider some of the differences in both genres. For example, although equally “inspired,” the gospels include certain narratives that are unanimously rejected as “unhistorical” by both Biblical scholars and historians alike. Stories like the slaughter of the innocents, the Magi, the Star of Bethlehem, and so on, are not considered to be historical. By contrast, the epistles never once mention the aforesaid stories, nor is there any mention of the Nativity, the virgin birth, the flight to Egypt, and the like. Why? Because the Epistles are NOT “theological.” They’re expository writings whose intention is to give us the “facts” as they really are!
Bottom line, the epistles give us a far more accurate picture of Jesus’ *visitation* than the gospels.
In conclusion, it appears that the gospels conceal Jesus far more effectively than they reveal him.
——-
Proof-text and Coherence Fallacies
The “proof-text fallacy” comprises the idea of putting together a number of out-of-context passages in order to validate a particular theological point that’s often disparagingly called “a private interpretation.” But, for argument’s sake, let’s turn these principles on their head. Classical Christianity typically determines heresy by assessing the latter’s overall view. If it doesn’t fit within the existing theological schema it is said to be heretical. Thus, dogmatic theology sets the theological standard against which all other theories are measured. They would argue that good exegesis doesn’t necessarily guarantee good theology, and can lead to a “coherence fallacy.” In other words, even if the exegesis of a string of proof-texts is accurate, the conclusion may not be compatible with the overall existing theology. This would be equivalent to a coherence fallacy, that is to say, the illusion of Biblical coherence.
By the same token, I can argue that traditional, historical-Jesus exegesis of certain proof-texts might be accurate but it may not fit the theology of an eschatological Christ, as we find in the epistles (e.g., Heb. 9.26b; 1 Pet. 1.20; Rev. 12.5). That would equally constitute a coherence fallacy. So, these guidelines tend to discourage independent proof-texting apart from a systematic coherency of Scripture. But what if the supposed canonical context is wrong? What if the underlying theological assumption is off? What then? So, the $64,000 question is, who can accurately determine the big picture? And who gets to decide?
For example, I think that we have confused Biblical literature with history, and turned prophecy into biography. In my view, the theological purpose of the gospels is to provide a fitting introduction to the messianic story *beforehand* so that it can be passed down from generation to generation until the time of its fulfillment. It is as though NT history is *written in advance* (cf. מַגִּ֤יד מֵֽרֵאשִׁית֙ אַחֲרִ֔ית [declaring the end from the beginning], Isa. 46.9-10; προεπηγγείλατο [promised beforehand], Rom. 1.2; προγνώσει [foreknowledge], Acts 2.22-23; προκεχειροτονημένοις [to appoint beforehand], Acts 10.40-41; ερχόμενα [things to come], Jn 16.13)!
So, if we exchange the theology of the gospels for that of the epistles we’ll find a completely different theology altogether, one in which the coherence of Scripture revolves around the *end-times*! For example, in 2 Pet. 1.16–21, all the explanations in vv. 16-18 are referring to the future. That’s why verse 19 concludes: “So we have the prophetic message more fully confirmed” (cf. 1 Pet. 1.10-11; 1 Jn 2.28).
In response, Dogmatic Theology would probably say that such a conclusion is at odds with the canonical context and that it seems to be based on autonomous proof-texting that is obviously out of touch with the broader theological teaching of Scripture. Really? So the so-called “teaching” of Scripture that Jesus died in Antiquity is a nonnegotiable, foregone conclusion? What if the basis upon which this gospel teaching rests is itself a proof-text fallacy that is out of touch with the teaching of the *epistles*? For example, there are numerous passages in the epistles that place the timeline of Jesus’ life (i.e., his birth, death, and resurrection) in *eschatological* categories (e.g., 2 Thess. 2.1-3; Heb. 1.1-2; 9.26b; 1 Pet. 1.10-11, 20; Rev. 12.5; 19.10d; 22.7). The epistolary authors deviate from the gospel writers in their understanding of the overall importance of •eschatology• in the chronology of Jesus. For them, Scripture comprises revelations and “prophetic writings” (see Rom. 16.25-26; 2 Pet. 1.19-21; Rev. 22.18-19). Therefore, according to the *epistolary literature*, Jesus is not a historical but rather an “eschatological” figure! Given that the NT epistles are part of the Biblical *canon,* their overall message holds equal value with that of the NT gospels, since they, too, are an integral part of the canonical context! To that extent, even the gospels concede that the Son of Man has not yet been revealed (see Lk. 17.30; cf. 1 Cor. 1.7; 1 Pet. 1.7)!
What is more, if the canonical context demands that we coalesce the different Biblical texts as if we’re reading a single Book, then the overall “prophetic” message of Revelation must certainly play an important role therein. The Book of Revelation places not only the timeline (12.5) but also the testimony to Jesus (19.10b) in “prophetic” categories:
I warn everyone who hears the words of the
prophecy of this book: if anyone adds to
them, God will add to that person the
plagues described in this book; if anyone
takes away from the words of the book of
this prophecy, God will take away that
person’s share in the tree of life and in the
holy city, which are described in this book
(Rev. 22.18-19 NRSV).
Incidentally, the Book of Revelation is considered to be an epistle. Thus, it represents, confirms, and validates the overarching *prophetic theme* or eschatological “theology” of the epistolary literature. That is not to say that the •theology• of the epistles stands alone and apart from that of the OT canon. Far from it! Even the *theology* of the OT confirms the earthy, end-time Messiah of the epistles (cf. Job 19.25; Isa. 2.19; Dan. 12.1-2; Zeph. 1.7-9, 15-18; Zech. 12.9-10)! As a matter of fact, mine is the *only* view that appropriately combines the end-time messianic expectations of the Jews with Christian Scripture!
Does this sound like a proof-text or coherence fallacy? If it does, it’s because you’re evaluating it from the theology of the gospels. If, on the other hand, you assess it using the theology of the epistles, it will seem to be in-context or in-sync with it. So, the theological focus and coherency of Scripture will change depending on which angle you view it from.
——-
Visions of the Resurrection
There are quite a few scholars that view the so-called resurrection of Christ not as a historical phenomenon but rather as a visionary experience. And this seems to be the theological message of the NT as well (cf. 2 Tim. 2.17-18; 2 Thess. 2.1-3). For example, Lk. 24.23 explicitly states that the women “had indeed seen a vision.” Lk. 24.31 reads: “he [Jesus] vanished from their sight.” And Lk. 24.37 admits they “thought that they were seeing a ghost.” Here are some of the statements that scholars have made about the resurrection, which do not necessarily disqualify them as believers:
The resurrection itself is not an event of
past history. All that historical criticism can
establish is that the first disciples came to
believe the resurrection (Rudolph
Bultmann, ‘The New Testament and
Mythology,’ in Kerygma and Myth: A
Theological Debate, ed. Hans Werner
Bartsch, trans. Reginald H. Fuller [London:
S.P.C.K, 1953-62], 38, 42).
When the evangelists spoke about the
resurrection of Jesus, they told stories
about apparitions or visions (John Dominic
Crossan, ‘A Long Way from Tipperary: A
Memoir’ [San Francisco:
HarperSanFransisco, 2000], 164-165).
At the heart of the Christian religion lies a
vision described in Greek by Paul as
ophehe—-“he was seen.” And Paul himself,
who claims to have witnessed an
appearance asserted repeatedly “I have
seen the Lord.” So Paul is the main source
of the thesis that a vision is the origin of the
belief in resurrection ... (Gerd Lüdemann,
‘The Resurrection of Jesus: History,
Experience, Theology.’ Translated by John
Bowden. [London: SCM, 1994], 97,
100).
It is undisputable that some of the followers
of Jesus came to think that he had been
raised from the dead, and that something
had to have happened to make them think
so. Our earliest records are consistent on
this point, and I think they provide us with
the historically reliable information in one
key aspect: the disciples’ belief in the
resurrection was based on visionary
experiences. I should stress it was visions,
and nothing else, that led to the first
disciples to believe in the resurrection (Bart
D. Ehrman, ‘How Jesus Became God: The
Exaltation of a Jewish Preacher from
Galilee’ [New York: Harper One, 2014],
183-184).
Ehrman sides with the *visionary language* that Luke, Bultmann, Crossan, and Lüdemann use. In the words of NT textual critic Kurt Aland:
It almost then appears as if Jesus were a
mere PHANTOM . . .
——-
Exegetical Application
I deliberately stay away from theology when I exegete Scripture precisely because it will taint the evidence with presuppositions, assumptions, and speculations that are not in the text. Thus, instead of focusing on the authorial intent hermeneutic, it will inevitably superimpose out-of-context meanings and create an eisegesis. All this, of course, is courtesy of confirmation bias.
So, I think one of the reasons why we’ve done so poorly in understanding, for example, the story of Jesus is because we have mixed-up exegesis with theology. When theology drives the exegesis, then the exegesis becomes blind and erroneous.
My method of exegesis is very simple. I see EXACTLY what the text *says,* EXACTLY *how* it says it. I don’t add or subtract anything, and I don’t speculate, guess, or theorize based on existing philosophies or theologies. The minute we go outside *the analogy of scripture,* that’s when we start to speculate. And that’s how we err. In short, let the Scriptures tell you what it means. Thus, the best interpretation is no interpretation at all!
——-
Conclusion
To find the truth, we must consider all the evidence objectively. Evangelicals, for instance, would be biased if they didn’t consider the academic standpoint even if, at times, it seems to be guided by liberal theology. In this way, they will be in a better position to consider objectively all the possibilities and probabilities regarding the correct interpretation of Scripture. That’s because the truth usually touches all points of view . . .
One of the exegetical stumbling blocks is our inability to view the gospels as “inspired metaphors.” Given their literary dependence on the OT, it appears as if the gospels themselves are “inspired parables.”
So, if the epistolary literature, which is both expositional and explicit, seems to contradict these so-called “theological parables,” then it becomes quite obvious that the “theology” of the gospels fails to meet scholarly and academic parameters. And, therefore, the epistolary literature must be given more serious attention and consideration!
Our exegetical shortcomings often stem from forced or anachronistic interpretations that are based on *theological speculation* and conjecture rather than on detailed exegesis. Even the Biblical translations themselves are not immune to the interpretative process, whether they be of dynamic or formal equivalence.
That’s why I have developed an exegetical system and have demonstrated the effectiveness of its approach to the study of the Biblical Christ. Accordingly, I argue that the epistles are the primary *keys* to unlocking the future timeline of Christ’s ***ONLY*** visitation! Hence, I leave you with one final rhetorical question:
What if the crucifixion of Christ is a future
event?

Textual Criticism: The Reliability of the New Testament
By Goodreads Author Eli Kittim
One has to be au courant with lower criticism to understand the significance and reliability of the New Testament. If we look at the number of extant NT manuscripts together with the relatively short period of time within which they were written (i.e, the time between the purported events and the written documents), no other book from Antiquity even comes close. First, we have over 5,800 manuscripts just in Greek (not counting those in other languages), more than any other book in history. Second, the texts were written within approximately two decades after the purported events. Other books have a much wider time-gap between the historical events and their initial documentations, as most were written hundreds of years later. Third, the New Testament has also been the most scrutinized book in all of literature. Its textual integrity has been relentlessly challenged down through the centuries. To date, no other book in history has been criticized and attacked as much as the New Testament. And yet its textual reliability has stood the test of time. Critical scholars still find it reliable! In fact, most of the variants are due to simple spelling errors, which do not significantly affect the meaning of the text. So, the textual reliability of the New Testament is well known among scholars. It’s the best attested book from the ancient world, as well as the bestseller of all time! And if you don’t think that it’s reliable, then you have no grounds to believe in Caesar, Homer, or Alexander the Great, whose biography, by the way, was written 400 years later! That’s how reliable the New Testament really is! In his blog, Bart Ehrman, the world-renowned textual scholar, writes:
“He [Bruce Metzger, Bart’s mentor] thought
that at the end of the day, we can be
reasonably confident of something like 99%
[reliability] of the text of the New
Testament. Textual scholars, in his
judgment, argue about that other 1%. As it
turns out, I don’t disagree with most of
that.”

How Did God Inspire the Biblical Authors?
By Goodreads Author Eli Kittim
Our Teacher Should Be the Holy Spirit
Before I venture out to expound on how Biblical “inspiration” occurs, it’s important to first say a few words about who determines the “meaning” of a text. In other words, where should we get our “hermeneutic” from? Should we draw it from our personal responses? Or should we conform to what the scholars say? But isn’t that still speculation and conjecture either way? Yes, it is! And it could be totally wrong, even if it’s a long-held consensus held by leading scholars! So what determines the meaning of a text? Is it Bible-study tools? No because they only give us a partial understanding. The short answer is: the Holy Spirit! Just as the Holy Spirit is responsible for “inspiring” the Biblical authors, so it is also responsible for communicating the “meaning” to its “recipients.” However, its recipients are not just anyone. They are neither those who openly profess to be “reborn” Christians nor those who post Facebook memes, “Repent or Go to Hell.” Rather, they’re the true, authentic Christians who don’t show off and hardly ever talk about their status as saved believers. Unbeknownst to the Cessationists, they hear from God “directly.” And they can interpret the Bible not based on current theological trends or methods of exegesis but on the word of the Spirit! So, they are “in the know.” Ideally, this is where the meaning of Scripture should come from! Bible-study tools won’t reveal these meanings no matter how sophisticated they might be. Now, let’s get back to the concept of Biblical “inspiration.”
Can the Bible Limit What God Can and Cannot Do?
There are many modern Biblical interpreters who hold to a form of “Pelagianism.” In ancient times, the Pelagian heresy comprised the Christian theological position that the human will alone is capable of choosing the good without the assistance of grace or any divine aid. Even Jesus’ salvific atonement becomes ultimately irrelevant in this view. These people, and I have met quite a few of them, don’t believe that the Spirit plays any significant role in our salvation. According to them, all we need to do is to follow the external dictates of the Bible. In this view, the Bible replaces God and thus becomes God-like, so to speak. Besides contradicting large portions of the New Testament, this position is also heretical in another way because it presents a counterfeit Christianity; that is to say, it presents the exact opposite of what authentic salvation truly consists of. It rejects inward spiritual experiences that lead to true “union” with God and promotes only an external form of obedience to rules and regulations. Jesus himself explains that such people don’t know God; they have neither heard from him nor do they know his “word”:
“You have never heard his voice or seen his
form, and you do not have his word abiding
in you, because you do not believe him
whom he has sent” (Jn 5.27-38).
Jesus nails it. Their erroneous doctrine is based on disbelief. In essence, they don’t even believe in Jesus. He goes on to say:
“You search the Scriptures because you
think that in them you have eternal life; it is
these that testify about Me” (Jn 5.39).
So, for them, the Bible has supplanted the Godhead and has become their “god.” It’s no longer God the Father, God the Son, or God the Holy Spirit who holds sway but rather the Bible per se and nothing but the Bible. That’s a form of idol-worship where “a means to an end” has suddenly become an end in itself! The King-James Only cult is a case in point!
The Dictation Theory
What is more, as far as Biblical inspiration is concerned, most modern scholars typically say that the Holy Spirit did not give the New Testament authors each and every word by dictation. To which I say, why not? They try desperately to fit in with the modern-secular, liberal culture that does not believe in supernatural phenomena and mocks all forms of divine communications. And yet, according to the Bible, these communications do exist (see 2 Tim. 3:16–17)!
The Bible stands or falls on the presence or absence of these divine communications. What ever happened to the Old Testament declaration: “Thus says the LORD”? Why water it down? Why dilute it to make it more palatable to the masses? Either God communicates with the human family or he doesn’t. In other words, either the Bible is the word of God or it isn’t. It’s that simple. By comparison, you’re either pregnant or you’re not. There’s no in between. Either God directly spoke to Isaiah and to Jeremiah or he didn’t. If he did, the Bible is transcribing divine communications. If he didn’t, then the Bible is the word of man. But if God indeed spoke to Isaiah, why couldn’t he equally speak to the Biblical authors, giving them the precise words audibly? After all, the authors themselves claimed to have heard God speak, saying, “This is my beloved Son, with whom I am well pleased” (Mt. 3.17). Besides, Jesus himself openly declares:
“For I did not speak on my own, but the
Father who sent me commanded me to say
all that I have spoken” (Jn 12.49).
If God has spoken directly in Isaiah 6.7, Jeremiah 26.2, Ezek. 28.2, John 2.1, 8, and also through Jesus (Jn 12.49), why wouldn’t he speak directly to the Biblical authors as well? It’s akin to when “Jeremiah called Baruch son of Neriah, and Baruch wrote on a scroll at Jeremiah's dictation all the words of the Lord that he had spoken to him” (Jer. 36.4).
The Dictation Theory Has Been Greatly Misunderstood
The reason most scholars don’t accept the dictation theory is because it seems to suggest that the Holy Spirit inscribed the words of Scripture through the agency of human authors who were somehow under God’s full control, in a state of passivity (perhaps in a trance), in which God dictated each and every word with perfect accuracy. In other words, scholars totally mischaracterize this communication process, as if they’re talking about zombies, automatons, people half-asleep, on sodium pentothal, under hypnosis, somnambulism, or the walking dead. In other words, the dictation theory has often been mistaken for the mechanical view of inspiration, such as automatic writing, and the like.
This mischaracterization and distortion stems from the fact that these scholars don’t yet fully understand what salvation really is, that is to say, what the relationship of the regenerated person to God consists of. Actually, by default, a regenerated person is already under the control of God, so that they don’t have to pass out or become an automaton in order to hear God’s voice. In other words, God communicates with them naturally, without restriction or interference, via a form of interpersonal communication while they are physically and cognitively stable, completely aware, and fully conscious! Therefore, the authentic, born-again Christians are already under God’s control and don’t need altered states of consciousness in order to hear God’s voice. Given that they are already sons of God (Jn 1.12-13), “born of the Spirit” of God (Jn 3.5-6), they hear God all the time (Jn 10.14, 27, 28)!
Stylistic Differences May Reflect the Source Rather Than the Authors
As for the argument pertaining to the stylistic differences between the New Testament authors, which suggests a variety of different personalities at work——consequently ruling out the possibility of verbatim-dictation from a single source——my reply is, why couldn’t the “stylistic differences” reflect the source rather than the authors? In other words, perhaps the texts reflect the Spirit itself——setting the context and content in various ways within the different compositions——rather than the individual personalities of the authors. After all, Heb. 1.1 says that “God spoke to our ancestors in many and various ways by the prophets.” That’s why we can find verbal agreements between disparate texts. For example, we read in the Old Testament narrative of Exodus 34.29 that Moses’ “face shone” (Hb. qaran; meaning “shine”) and then, lo and behold, we find the exact same equivalent words used in the Greek New Testament (Matthew 17.2) to say that Jesus’ “face shone” (Gk. ἔλαμψεν; meaning “shine”). Two completely different authors with completely different writing styles and languages, writing from two completely different time periods and locations, with over 1,000 years separating the two texts, and yet we find verbal agreements! Why? Same source; same Spirit dictating the exact same words through different languages and styles. Such verbal agreements and parallels abound in Scripture. Otherwise, if it was left up to each and every individual author to write whatever they wanted, then it would obviously be the word of man and should not be accepted as the word of God.
Biblical Interpretation Should Be Based Entirely on Biblical Inspiration
Furthermore, Biblical interpretation should be based entirely on the Spirit, not on guess-work. Being partly-right doesn’t cut it because it implies that we may also be partly-wrong. Either we know what’s going on or we don’t:
“When the Spirit of truth comes, he will guide
you into all the truth; for he will not speak on
his own, but will speak whatever he hears,
and he will declare to you the things that
are to come [ἐρχόμενα]” (Jn 16.13).
In other words, those who are indwelt by the Spirit walk by the Spirit and are constantly informed by the Spirit who guides them “into all the truth.”
Conclusion
Therefore, based on the aforementioned reasons, it seems indisputable that the Spirit of God inspired the Biblical authors by giving them each and every word by dictation. For God speaks to us directly, but only those who belong to him can actually hear his voice. The following quote demonstrates that Scripture (which is almost entirely prophetic) was not left to the discretion of the individual authors but that the authors were “carried along by the Holy Spirit” when they “spoke from God”:
“for no prophecy was ever produced by the
will of man, but men carried along by the
Holy Spirit spoke from God” (2 Pet. 1.21).
——-
This is the PDF of my article——published in the Journal of Higher Criticism, volume 13, number 3 (Fall 2018)——entitled, The Birth, Death, and Resurrection of Christ According to the Greek New Testament Epistles.

Should Our Prayers Be Offered to Jesus or to the Saints?
By Author Eli Kittim
The Communion of Saints
Intercession of the saints plays a crucial role in the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox churches. This practice is derived from the Catholic creed of the Communion of saints. The said doctrine holds that dead saints pass instantly into the divine presence and therefore have a sort of fiduciary power in helping others to procure favors and blessings. This is not unlike Shinto, a Japanese religion that incorporates the worship of ancestors. In fact, the Christian patron saints that act as intermediaries between God and humans, interceding for trade, agriculture, health, and so on, are reminiscent of the Greek pantheon of demigods (The Twelve Olympians) in which each deity was responsible for a particular aspect of life. In this sense, the church adopted a form of pagan polytheism. The specific dedications and remembrances of saints in the Catholic, and especially in the Orthodox, churches have been highly developed to such an extent that the entire liturgical year is devoted to and structured around the so-called calendar of saints, in which each day pays homage to a particular saint(s) (i.e. feast day). Not to mention the ancient preoccupation with saints' relics and the lucrative pilgrimages that have been designed for such worship.
Do the Saints in Heaven Pray for the People on Earth?
Much to our dismay, saints in heaven don’t pray on behalf of earthlings. Rather, these martyrs pray for God to avenge their blood (Rev. 6.9-10 NRSV):
When he opened the fifth seal, I saw under
the altar the souls of those who had been
slaughtered for the word of God and for the
testimony they had given; they cried out
with a loud voice, ‘Sovereign
Lord, holy and true, how long will it be
before you judge and avenge our blood on
the inhabitants of the earth?’
Similarly, “the prayers of the saints” in Rev. 5.8-10 are solely directed to Jesus, praising him for his extraordinary feats. They’re not about helping John Doe, back on earth, with his financial woes, or Jane Doe with her marital breakdown. Rev. 5.8-10 reads:
When he had taken the scroll, the four living
creatures and the twenty-four elders fell
before the Lamb, each holding a harp and
golden bowls full of incense, which are the
prayers of the saints. They sing a new song:
‘You are worthy to take the scroll and to
open its seals, for you were slaughtered and
by your blood you ransomed for God saints
from every tribe and language and people
and nation; you have made them to be a
kingdom and priests serving our God, and
they will reign on earth.’
Incidentally, the so-called “saints” in Rev. 5.8 are not an elite, hierarchical class of people worthy of worship. That’s a misnomer. On the contrary, all who are *born-again* in Christ are called “saints” (cf. Rom. 1.7). Remember, not even angels are allowed to be worshipped in God’s kingdom (see Rev. 19.10), let alone departed spirits.
Is Praying to Saints Biblical?
Over against the intercessory prayer of saints is Deut. 18.11 which explicitly forbids those who consult the dead (cf. Isa. 8.19). That’s precisely why, in the parable of the Rich man and Lazarus (Luke 16:19–31), the rich man’s intercessory-prayer request is denied!
Sometimes Catholic and Orthodox writers will point to Old Testament accounts in which patriarchs or prophets enlisted the help of an angel (e.g. Gen. 48.16; Zech. 1.8-11). But they fail to mention that the said angel is typically associated with the angel of the Lord, which is traditionally viewed by Christian commentators as the Pre-Incarnate Son (cf. Gen. 16.7; Exod. 33.14; Jer. 1.4). Furthermore, conversing with an angel is not the same as praying to an angel. Yet in defense of intercessory prayer of heavenly beings, Catholic writers often point to the Annunciation as a case in point. But again, Mary’s conversation with Gabriel does not involve an intercessory prayer request, nor an act of prostration or worship.
The Catholic commentariat has also presented several examples from the New Testament to make their point. For instance, they cite Rev. 8.3, namely, the prayers of the saints that rise up before God. However, the context of this eschatological verse is God’s wrath that is poured out upon the earth, not an answer to our prayers (Rev. 8.3-5):
Another angel with a golden censer came
and stood at the altar; he was given a great
quantity of incense to offer with the prayers
of all the saints on the golden altar that is
before the throne. And the smoke of the
incense, with the prayers of the saints, rose
before God from the hand of the angel.
Then the angel took the censer and filled it
with fire from the altar and threw it on the
earth; and there were peals of thunder,
rumblings, flashes of lightning, and an
earthquake.
Human Intercession versus Intercession of saints
The fact that there is a body of Christ (“a cloud of witnesses” Heb. 12.1) is not an invitation or a request to worship them. Catholic scholars have confused the issue even further. They cite various instances in the New Testament in which Paul commands Christians to pray for him (e.g. 2 Cor. 1.11). Or they’ll cite the example of Timothy who commands Christians to pray for one another (1 Tim. 2.1). However, praying “FOR” someone and praying “TO” someone are two completely different things. To pray “for” (or on behalf of) a living person is one thing. To pray “to” a dead person is quite another. In the first case, you’re simply praying *for* the living (human intercession) and asking God to help them in their time of need. However, praying *to* a deceased saint for help is a different matter altogether. Now, you are praying not to God but *to* a dead saint (Intercession of Saints) to help a living human being. As a result, the saints have gained so much power that they have become intercessors between heaven and earth. It’s true that Paul and Timothy instructed Christians to pray for the betterment of others. But that’s not the same as praying to dead saints for help, grace, and blessings.
Although Protestant denominations accept human intercessory prayer for the living (cf. Rom. 15.30), they deny the intercession of the dead on behalf of the living. Similarly, Reformed theologians acknowledge that the “communion of saints" comprise all who are in Christ, including the departed. Nevertheless, in their view, invocations of the departed spirits of saints constitute a transgression of the First Commandment (see Deut. 5.7): “You shall have no other gods before me.”
On the Importance of Developing a Personal Relationship with Christ
The Catholic and Orthodox mindset is that God is not in competition with his creation (Robert Barron), and that although Christ is humanity’s mediator via the cross (1 Tim. 2.5), he’s not necessarily accessible as our 24-7 prayer advocate on a minute-by-minute basis. He has partners and associates that work under him, much like a high-end law firm in New York. But the so-called “managing partner” (i.e. Law firm CEO) at the top is usually inaccessible. Hence the need for the intercessory prayers. They argue that turning to the saints for help is not in competition with Jesus Christ since God has many partners and friends and is the ultimate source of all living things.
But this represents a distortion of Biblical revelation. The multiple attestations of the New Testament are all about Jesus. They feature Jesus as the leading figure, who is the hero of the story, and without whom we cannot be saved. It is the story of the creator who enters creation. He is the one “through whom he [God] also created the worlds” (Heb. 1.2). John’s gospel attests of his divinity: “In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God” (1.1). Paul declares: “For in him the whole fullness of deity dwells bodily” (Col. 2.9). And without the shedding of his blood there can be no New Testament, much less a church (cf. Heb. 9.17, 22). Phil. 2.10-11 concludes:
so that at the name of Jesus every knee
should bend, in heaven and on earth and
under the earth, and every tongue should
confess that Jesus Christ is Lord, to the
glory of God the Father.
In Mt. 28.18, the Matthean Jesus exclaims:
All authority in heaven and on
earth has been given to me.
In Rev 1.8, Jesus is equated with God Almighty:
‘I am the Alpha and the Omega,’
says the Lord God, who is and
who was and who is to come,
the Almighty.
In Isaiah chapter 42 verse 8, God says:
I am the Lord, that is my name; my glory I
give to no other, nor my praise to idols.
With Jesus’ extraordinary credentials and qualifications, why should we consult the spirits of dead men? The point is that Jesus is everything to regenerated Christians. He’s constantly on their mind. Born-again Christians are madly in love because of what Jesus has done for them, namely, he has made them *fully alive,* while their cup is running over with love, peace of mind, and perpetual bliss! Hence, there’s a fire of love for Jesus that burns inside every born-again-Christian’s heart. So, your focus should not be diluted on secondary figures and causes. Rather, your attention must be concentrated on Christ alone, if you are to “be transformed by the renewing of your minds” (Rom. 12.2). That’s because there is only *one* mediator (not two or three) between God and humanity——“the man Christ Jesus” (1 Tim. 2.5). Therefore, when religion tries to seduce you into chasing after idols, you must run the other way.
Is the Intercession of the Saints Blasphemy?
Dr. Edward Sri——theologian, author, and prominent Catholic speaker who appears regularly on EWTN——wrote a paper entitled, “What Does the Bible Say about Praying to Saints?” The article concludes as follows:
How to Grow in Fellowship with the Saints
1. Pick a few saints that you want to get to know.
2. Read their writings and learn about their lives. Fill your mind with their stories and their example.
3. Talk to those saints, every day. Share your weaknesses with them and ask them to walk with you in your difficult times. Don’t just ask them to pray for you…invite them to be with you in every part of your life.
This borders on blasphemy. The point of Sri’s exhortation is that instead of developing a personal relationship with Jesus, we are encouraged to develop an intimate relationship with a beloved saint of our choosing. In other words, the aforesaid article is strongly urging people to devote themselves to someone other than Christ (in fact, a departed spirit) and to focus all their energies on the said saint. It is a clever, if not demonic, deception to remove our focus away from Christ under cloak of religion (2 Cor. 11.14):
And no wonder! Even Satan disguises
himself as an angel of light.
——-

There Was No Pre-Pauline Oral Tradition
By Eli Kittim 🎓
When asked why Paul didn’t give us more details about Jesus’ existence, some scholars often use a common strawman argument that everyone already knew the story and so Paul didn’t have to write anything about it. But after thinking about this explanation for some time, I didn’t find it convincing. A key problem besetting the assumed pre-Pauline tradition is that it is a) based entirely on the gospel literature, which came much later, and b) it hasn’t been verified because there were no eyewitnesses and no firsthand accounts. Plus, the stories that we’re all familiar with (from the gospels) were not written until a few decades after Paul’s writings. So the life of Jesus was not written before, but after, Paul. Given that Paul’s knowledge of the story of Jesus is based entirely on “a revelation,” and that Paul himself admits that he didn’t receive it from man, nor was he taught it (Gal 1:11-12), it’s reasonable to assume that no one else knew the story prior to Paul’s writings, at least from a literary standpoint. After all, Paul was the first to write about it!
There are a lot of presuppositions that are implied by the oral Pre-Pauline-tradition hypothesis that most people aren’t aware of. Many people also presuppose that the gospels are historical, even though that has not been verified either. On the contrary, the fact that they were anonymously written, and that there were no eyewitnesses and no firsthand accounts, and that the events in Jesus’ life were, for the most part, borrowed from the Old Testament, seems to suggest that they were written in the literary genre known as “theological fiction.”
What is more, because the gospel texts are found at the beginning of the New Testament, people often presuppose that the gospels were the first Christian writings, and so they completely misunderstand the New Testament literary chronology. This presupposition leads to many other false assumptions that are very misleading and totally unrelated to the actual chronological development of the New Testament writings.
They have it all backwards❗️
What is more, because of the hypothetical Q source (for which there’s no evidence), even scholars often talk as if the gospels preceded the epistles, and so given that everyone already knew about the story, Paul didn’t have to mention all the details…
But wait just a second… ⛔️
The full-fledged story we usually refer to actually starts around 70 AD with Mark, and ends at the end of the first century with John. But surprise surprise, Paul is writing much much earlier than that. Paul’s letters are the FIRST Christian writings, which are written over two decades earlier (49-50 AD)! Paul’s writings are actually the EARLIEST Christian writings. So, presumably, no one knew the story yet, at least from a literary perspective. It was Paul’s task to tell the reader all about it.
But Paul failed to mention the pertinent information regarding the details of Jesus’ life, even though it is assumed that he was in a position to know this information. If Paul was expected to have all the pertinent information regarding the Jesus-story, and intending to write a complete account of these events, and if the details of the Jesus-story were important enough to deserve to be mentioned, then why didn’t Paul talk about any of them? Astoundingly, Paul didn’t mention any of the legendary elements that we find in the later embellishments of the 70s, 80s, and 90s. In Paul’s letters, there’s no nativity, no virgin birth, no shepherds, no star of Bethlehem, no magi, no census, no Elizabeth, no Zechariah, no John the Baptist, no flight to Egypt, no slaughter of the innocents, nothing about
“Jesus healing anyone,
casting out a demon, doing any other
miracle, arguing with Pharisees or
other leaders, teaching the multitudes, even
speaking a parable, being baptized, being
transfigured, going to Jerusalem, being
arrested, put on trial, found guilty of
blasphemy, appearing before Pontius Pilate
on charges of calling himself the King of the
Jews, being flogged, etc. etc. etc. It’s a very,
very long list of what he doesn’t tell us
about.” —Source credit: Bart D. Ehrman
This doesn’t mean that Paul is writing letters to people who already knew about the story.
It means that such a story didn’t exist. It was added later!
Conclusion
How is a supposed Aramaic story suddenly taken over, less than 2 decades after the purported events, by highly articulate Greeks and written about in other countries, such as Greece and Rome? None of the New Testament books were ever written in Palestine by Jews! That doesn’t make any sense and it certainly casts much doubt about the idea of a supposed Aramaic oral tradition.
In fact, most of the New Testament Books were written in Greece: Romans, 1 & 2 Corinthians, Galatians, 1 & 2 Thessalonians, 1 Timothy, Titus, the Book of Revelation, and possibly others as well! To sum up, most of the New Testament Books were composed in Greece. Most of the epistles were penned in Greece and addressed to Greek communities. The New Testament was written exclusively in Greek, outside of Palestine, by “Greek” authors who copied the Greek Septuagint rather than the Hebrew Bible when quoting from the Old Testament. So where is the Aramaic tradition?

The Da Vinci Code Versus The Gospels
By Eli Kittim 🎓
Bart Ehrman was once quoted as saying: “If Jesus did not exist, you would think his brother would know it.” This is an amusing anecdote that I’d like to use as a springboard for this short essay to try to show that it’s impossible to separate literary characters from the literature in which they are found. For example, when Ehrman says, “If Jesus did not exist, you would think his brother would know it,” his comment presupposes that James is a real historical figure. But how can we affirm the historicity of a literary character offhand when the so-called “history” of this character is solely based on, and intimately intertwined with, the literary New Testament structures? And if these literary structures are not historical, what then? The fact that the gospels were written anonymously, and that there were no eyewitnesses and no firsthand accounts, and that the events in Jesus’ life were, for the most part, borrowed from the Old Testament, seems to suggest that they were written in the literary genre known as theological fiction. After all, the gospels read like Broadway plays!
Let me give you an analogy. Dan Brown writes novels. All his novels, just like the gospels, contain some historical places, figures, and events. But the stories, in and of themselves, are completely fictional. So, Ehrman’s strawman argument is tantamount to saying that if we want to examine the historicity of Professor Robert Langdon——who is supposedly a Harvard University professor of history of art and symbology——we’ll have to focus on his relationship with Sophie Neveu, a cryptologist with the French Judicial Police, and the female protagonist of the book. Ehrman’s earlier anecdote would be akin to saying: “if Robert Langdon did not exist, you would think Sophie would know it.”
But we wouldn’t know about Robert Langdon if it wasn’t for The Da Vinci Code. You can’t separate the character Robert Langdon from The Da Vinci Code and present him independently of it because he’s a character within that book. Therefore, his historicity or lack thereof depends entirely on how we view The Da Vinci Code. If The Da Vinci Code turns out to be a novel (which in fact it is), then how can we possibly ask historians to give us their professional opinions about him? It’s like asking historians to give us a historical assessment of bugs bunny? Was he real? So, as you can see, it’s all based on the literary structure of The Da Vinci Code, which turns out to be a novel!
By comparison, the historicity of Jesus depends entirely on how we view the literary structure of the gospel literature. Although modern critical scholars view the gospels as theological documents, they, nevertheless, believe that they contain a historic core or nucleus. They also think that we have evidence of an oral tradition. We do not! There are no eyewitnesses and no firsthand accounts. All we have about the life and times of Jesus are the gospel narratives, which were composed approximately 40 to 70 years after the purported events by anonymous Greek authors who never met Jesus. And they seem to be works of theological fiction. So where is the historical evidence that these events actually happened? We have to believe they happened because the gospel characters tell us so? It’s tantamount to saying that the events in The Da Vinci Code actually happened because Robert Langdon says so. But if the story is theological, so are its characters. Thus, the motto of the story is: don’t get caught up in the characters. The message is much more important! As for those who look to Josephus’ Antiquities for confirmation, unfortunately——due to the obvious interpolations——it cannot be considered authentic. Not to mention that Josephus presumably would have been acquainted with the gospel stories, most of which were disseminated decades earlier.
Don’t get me wrong. I’m not trying to downplay the seriousness of the gospel message. I’m simply trying to clarify it. The gospels are inspired, but they were never meant to be taken literally. I’m also a believer and I have a high view of scripture. The message of Christ is real. But when will the Jesus-story play out is not something the gospels can address. Only the epistles give us the real Jesus!