Language - Tumblr Posts
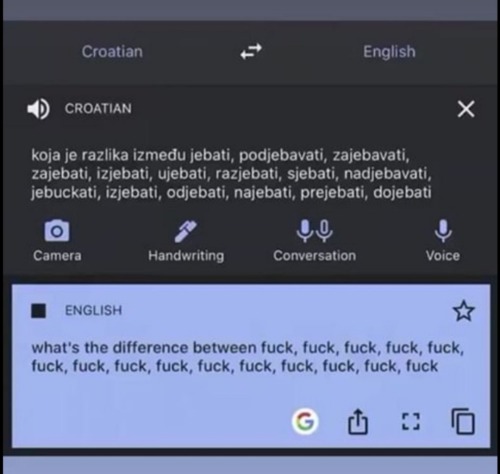
fun fact about languages: a linguist who was studying aboriginal languages of Australia finally managed to track down a native speaker of the Mbabaram language in the 60s for his research. they talked a bit and he started by asking for the Mbabaram word for basic nouns. They went back and forth before he asked for the word for “dog” The man replied “dog” They had a bit of a “who’s on first” moment before realizing that, by complete coincidence, Mbabaram and English both have the exact same word for dog.

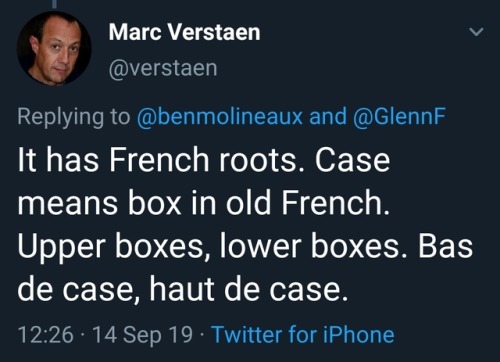
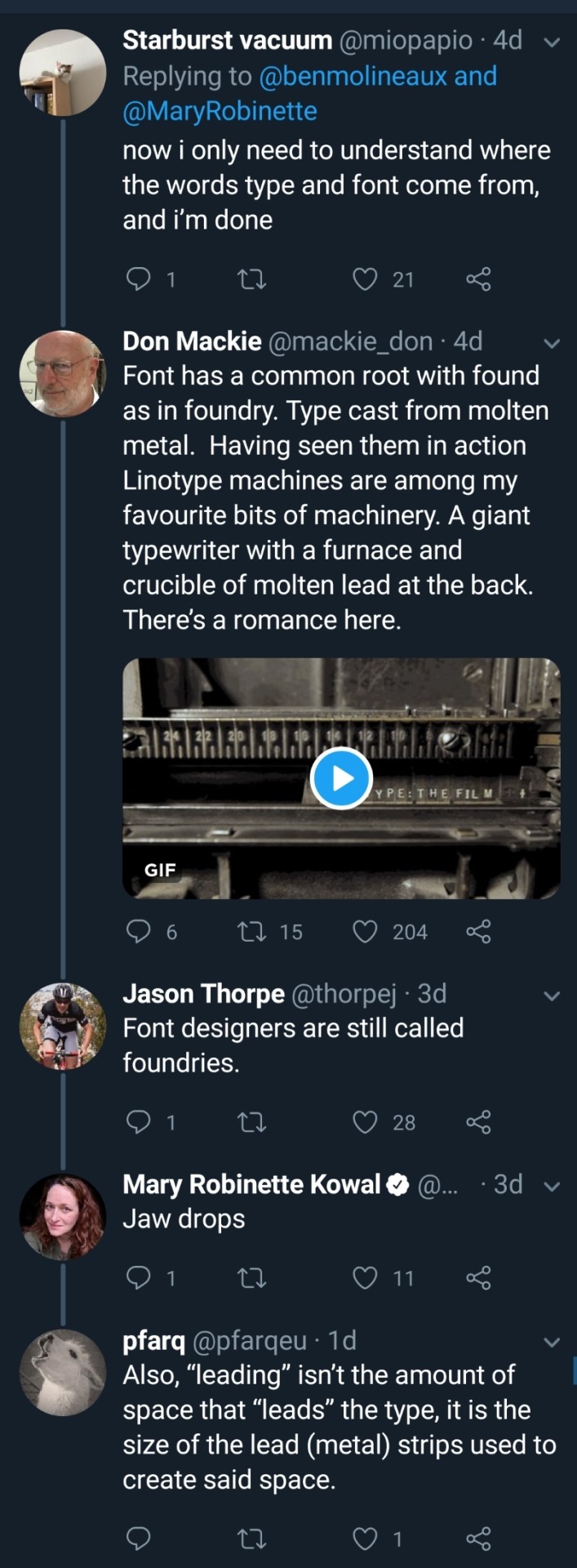
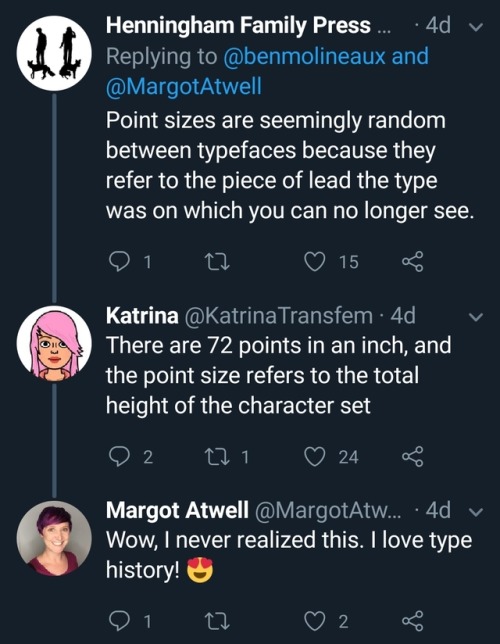

TiL (click to go to the thread, which probably has more interesting tidbits I missed).
Bonus:


Does anyone have any good books, shows, apps, websites and stuff to learn Tamil???? I specifically want to learn Eelam tamil(the Sri Lankan tamil dialect) but everything I find is manly in nabu tamil. So Help please??
I JUST LITERALLY IMAGINE MOON YEETING A CHILD
SUN/MOONDROP HEADCANNONS
I love them
both of them will screech at you for language like BadBoyHalo
They have bandaids in their chest compartments and they're rainbow (Moon's are space themed)
Moon leave little gifts for Sunny sometimes and makes sure there's always plenty of glitter glue and craft supplies
He does have to hide the fizzy fazz though, otherwise Sunny will drink too much
Moon likes to sleep at the bottom of the ball pit
Sunny's room is filled with just about every type of light source--candles, fairy lights, leds, lamps, etc.
the human employees don't know how absolutely terrifying Moon is (I love him anyway tho), so they just think Sunny is afraid of the dark as part of his programming to connect with the kids
Sun/Moon's personality switch being so drastic wasn't intended, the chip got damaged on it's way to the pizzaplex
Roxy’s chip came with it and was also in the accident but suffered less damage
the "beautiful/handsom, whichever you prefer" tik tok sound is actually something Sunny does. He also asks for pronouns
He/xe Sunny
They/it Moon
Sometimes Moon plays pranks on Sunny and the guards. They're...mostly harmless
Sundrop has infinite patience and empathy
Moondrop would yeet a child if it didn't stfu quickly
They're both programmed to recognize signs of child abuse
I have been learning Russian for two and a half months ("I wanna read Dostoyevsky in the original" - the queen's gambit) and it's such a simple language, apart from the pronouns.
Pronouns are horrible in Russian :(
Stay yourself, stay curious
Give me a word and I'll translate it to one of the oldest languages - Hebrew!
Any word!!!!!!! ヽ(*゚ー゚*)ノ
Stay yourself, stay curious

Someone asked me to expand a little on a topic that was buried down in a big chain of reblogs, so I'm doing that here--it's about the use of the archaic "thee", "thou", "thy", etc. in LOTR and what it tells you about characters’ feelings for one another. (I am NOT an expert on this, so it's just what I've picked up over time!)
Like many (most?) modern English speakers, I grew up thinking of those old forms of 2nd person address as being extra formal. I think that's because my main exposure to them was in the Bible ("thou shall not...") and why wouldn't god, speaking as the ultimate authority, be using the most formal, official voice? But it turns out that for a huge chunk of the history of the English language, "thee," "thou," and "thy" were actually the informal/casual alternatives to the formal "you", “your”, “yours”. Like tú v. usted in Spanish!
With that in mind, Tolkien was very intentional about when he peppered in a "thee" or a "thou" in his dialogue. It only happens a handful of times. Most of those are when a jerk is trying to make clear that someone else is beneath them by treating them informally. Denethor "thou"s Gandalf when he’s pissed at him. The Witch King calls Éowyn "thee" to cut her down verbally before he cuts her down physically. And the Mouth of Sauron calls Aragorn and Gandalf "thou" as a way to show them that he has the upper hand. (Big oops by all 3 of these guys!)
The other times are the opposite--it's when someone starts to use the informal/casual form as a way to show their feeling of affection for someone else. Galadriel goes with the formal "you" all through the company's days in Lórien, but by the time they leave she has really taken them to heart. So when she sends them a message via Gandalf early in the Two Towers, she uses "thee" and "thou" in her words to Aragorn, Legolas and Gimli because now they're valued friends and allies. And--this is the big one, folks, that was already alluded to in my previous post--Éowyn starts aggressively "thou"ing Aragorn when she is begging him to take her along as he prepares to ride out of Dunharrow. She is very intentionally trying to communicate her feelings to him in her choice of pronoun--an "I wouldn't be calling you "thee" if I didn't love you" kind of thing. And he is just as intentionally using "you" in every single one of his responses in order to gently establish a boundary with her without having to state outright that he doesn't reciprocate her feelings. It's not until much later when her engagement to Faramir is announced that Aragorn finally busts out "I have wished thee joy ever since I first saw thee". Because now it is safe to acknowledge a relationship of closeness and familiarity with her without the risk that it will be misinterpreted. He absolutely wants to have that close, familiar relationship, but he saved it for when he knew she could accept it on his terms without getting hurt.
So, you know, like all things language-based...Tolkien made very purposeful decisions in his word choices down to a bonkers level of detail. I didn’t know about this pronoun thing until I was a whole ass adult, but that’s the joy of dealing with Tolkien. I still discover new things like this almost every time I re-read.
Okay, so:
Latin has this word, sic. Or, if we want to be more diacritically accurate, sīc. That shows that the i is long, so it’s pronounced like “seek” and not like “sick.”
You might recognize this word from Latin sayings like “sic semper tyrannis” or “sic transit gloria mundi.” You might recognize it as what you put in parentheses when you want to be pass-agg about someone’s mistakes when you’re quoting them: “Then he texted me, ‘I want to touch you’re (sic) butt.’”
It means, “thus,” which sounds pretty hoity-toity in this modren era, so maybe think of it as meaning “in this way,” or “just like that.” As in, “just like that, to all tyrants, forever,” an allegedly cool thing to say after shooting a President and leaping off a balcony and shattering your leg. “Everyone should do it this way.”
Anyway, Classical Latin somewhat lacked an affirmative particle, though you might see the word ita, a synonym of sic, used in that way. By Medieval Times, however, sic was holding down this role. Which is to say, it came to mean yes.
Ego: Num edisti totam pitam?
Tu, pudendus: Sic.
Me: Did you eat all the pizza?
You, shameful: That’s the way it is./Yes.
This was pretty well established by the time Latin evolved into its various bastard children, the Romance languages, and you can see this by the words for yes in these languages.
In Spanish, Italian, Asturian, Catalan, Corsican, Galician, Friulian, and others, you say si for yes. In Portugese, you say sim. In French, you say si to mean yes when you’re contradicting a negative assertion (”You don’t like donkey sausage like all of us, the inhabitants of France, eat all the time?” “Yes, I do!”). In Romanian, you say da, but that’s because they’re on some Slavic shit. P.S. there are possibly more Romance languages than you’re aware of.
But:
There was still influence in some areas by the conquered Gaulish tribes on the language of their conquerors. We don’t really have anything of Gaulish language left, but we can reverse engineer some things from their descendants. You see, the Celts that we think of now as the people of the British Isles were Gaulish, originally (in the sense that anyone’s originally from anywhere, I guess) from central and western Europe. So we can look at, for example, Old Irish, where they said tó to mean yes, or Welsh, where they say do to mean yes or indeed, and we can see that they derive from the Proto-Indo-European (the big mother language at whose teat very many languages both modern and ancient did suckle) word *tod, meaning “this” or “that.” (The asterisk indicates that this is a reconstructed word and we don’t know exactly what it would have been but we have a pretty damn good idea.)
So if you were fucking Ambiorix or whoever and Quintus Titurius Sabinus was like, “Yo, did you eat all the pizza?” you would do that Drake smile and point thing under your big beefy Gaulish mustache and say, “This.” Then you would have him surrounded and killed.
Apparently Latin(ish) speakers in the area thought this was a very dope way of expressing themselves. “Why should I say ‘in that way’ like those idiots in Italy and Spain when I could say ‘this’ like all these cool mustache boys in Gaul?” So they started copying the expression, but in their own language. (That’s called a calque, by the way. When you borrow an expression from another language but translate it into your own. If you care about that kind of shit.)
The Latin word for “this” is “hoc,” so a bunch of people started saying “hoc” to mean yes. In the southern parts of what was once Gaul, “hoc” makes the relatively minor adjustment to òc, while in the more northerly areas they think, “Hmm, just saying ‘this’ isn’t cool enough. What if we said ‘this that’ to mean ‘yes.’” (This is not exactly what happened but it is basically what happened, please just fucking roll with it, this shit is long enough already.)
So they combined hoc with ille, which means “that” (but also comes to just mean “he”: compare Spanish el, Italian il, French le, and so on) to make o-il, which becomes oïl. This difference between the north and south (i.e. saying oc or oil) comes to be so emblematic of the differences between the two languages/dialects that the languages from the north are called langues d’oil and the ones from the south are called langues d’oc. In fact, the latter language is now officially called “Occitan,” which is a made-up word (to a slightly greater degree than that to which all words are made-up words) that basically means “Oc-ish.” They speak Occitan in southern France and Catalonia and Monaco and some other places.
The oil languages include a pretty beefy number of languages and dialects with some pretty amazing names like Walloon, and also one with a much more basic name: French. Perhaps you’ve heard of it, n'est-ce pas?
Yeah, eventually Francophones drop the -l from oil and start saying it as oui. If you’ve ever wondered why French yes is different from other Romance yeses, well, now you know.
I guess what I’m getting at is that when you reblog a post you like and tag it with “this,” or affirm a thing a friend said by nodding and saying “Yeah, that”: you’re not new
It's still kinda wild how Phineas and Ferb managed to completely hijack an idiom. Now whenever someone hears a sentence leading with "If I had a nickel for everytime [...]", odds are their brain auto fills with "I'd have two nickels. Which isn't a lot, but it's weird that it happened twice," rather than "I'd be rich," or "I could [action that requires purchasing something requiring an obscene amount of money]". Y'know, what the idiom originally was
A Guide to Historically Accurate Regency-Era Names

I recently received a message from a historical romance writer asking if I knew any good resources for finding historically accurate Regency-era names for their characters.
Not knowing any off the top of my head, I dug around online a bit and found there really isn’t much out there. The vast majority of search results were Buzzfeed-style listicles which range from accurate-adjacent to really, really, really bad.
I did find a few blog posts with fairly decent name lists, but noticed that even these have very little indication as to each name’s relative popularity as those statistical breakdowns really don't exist.
I began writing up a response with this information, but then I (being a research addict who was currently snowed in after a blizzard) thought hey - if there aren’t any good resources out there why not make one myself?
As I lacked any compiled data to work from, I had to do my own data wrangling on this project. Due to this fact, I limited the scope to what I thought would be the most useful for writers who focus on this era, namely - people of a marriageable age living in the wealthiest areas of London.
So with this in mind - I went through period records and compiled the names of 25,000 couples who were married in the City of Westminster (which includes Mayfair, St. James and Hyde Park) between 1804 to 1821.
So let’s see what all that data tells us…
To begin - I think it’s hard for us in the modern world with our wide and varied abundance of first names to conceive of just how POPULAR popular names of the past were.
If you were to take a modern sample of 25-year-old (born in 1998) American women, the most common name would be Emily with 1.35% of the total population. If you were to add the next four most popular names (Hannah, Samantha, Sarah and Ashley) these top five names would bring you to 5.5% of the total population. (source: Social Security Administration)
If you were to do the same survey in Regency London - the most common name would be Mary with 19.2% of the population. Add the next four most popular names (Elizabeth, Ann, Sarah and Jane) and with just 5 names you would have covered 62% of all women.
To hit 62% of the population in the modern survey it would take the top 400 names.
The top five Regency men’s names (John, William, Thomas, James and George) have nearly identical statistics as the women’s names.
I struggled for the better part of a week with how to present my findings, as a big list in alphabetical order really fails to get across the popularity factor and also isn’t the most tumblr-compatible format. And then my YouTube homepage recommended a random video of someone ranking all the books they’d read last year - and so I present…
The Regency Name Popularity Tier List
The Tiers
S+ - 10% of the population or greater. There is no modern equivalent to this level of popularity. 52% of the population had one of these 7 names.
S - 2-10%. There is still no modern equivalent to this level of popularity. Names in this percentage range in the past have included Mary and William in the 1880s and Jennifer in the late 1970s (topped out at 4%).
A - 1-2%. The top five modern names usually fall in this range. Kids with these names would probably include their last initial in class to avoid confusion. (1998 examples: Emily, Sarah, Ashley, Michael, Christopher, Brandon.)
B - .3-1%. Very common names. Would fall in the top 50 modern names. You would most likely know at least 1 person with these names. (1998 examples: Jessica, Megan, Allison, Justin, Ryan, Eric)
C - .17-.3%. Common names. Would fall in the modern top 100. You would probably know someone with these names, or at least know of them. (1998 examples: Chloe, Grace, Vanessa, Sean, Spencer, Seth)
D - .06-.17%. Less common names. In the modern top 250. You may not personally know someone with these names, but you’re aware of them. (1998 examples: Faith, Cassidy, Summer, Griffin, Dustin, Colby)
E - .02-.06%. Uncommon names. You’re aware these are names, but they are not common. Unusual enough they may be remarked upon. (1998 examples: Calista, Skye, Precious, Fabian, Justice, Lorenzo)
F - .01-.02%. Rare names. You may have heard of these names, but you probably don’t know anyone with one. Extremely unusual, and would likely be remarked upon. (1998 examples: Emerald, Lourdes, Serenity, Dario, Tavian, Adonis)
G - Very rare names. There are only a handful of people with these names in the entire country. You’ve never met anyone with this name.
H - Virtually non-existent. Names that theoretically could have existed in the Regency period (their original source pre-dates the early 19th century) but I found fewer than five (and often no) period examples of them being used in Regency England. (Example names taken from romance novels and online Regency name lists.)
Just to once again reinforce how POPULAR popular names were before we get to the tier lists - statistically, in a ballroom of 100 people in Regency London: 80 would have names from tiers S+/S. An additional 15 people would have names from tiers A/B and C. 4 of the remaining 5 would have names from D/E. Only one would have a name from below tier E.
Women's Names
S+ Mary, Elizabeth, Ann, Sarah
S - Jane, Mary Ann+, Hannah, Susannah, Margaret, Catherine, Martha, Charlotte, Maria
A - Frances, Harriet, Sophia, Eleanor, Rebecca
B - Alice, Amelia, Bridget~, Caroline, Eliza, Esther, Isabella, Louisa, Lucy, Lydia, Phoebe, Rachel, Susan
C - Ellen, Fanny*, Grace, Henrietta, Hester, Jemima, Matilda, Priscilla
D - Abigail, Agnes, Amy, Augusta, Barbara, Betsy*, Betty*, Cecilia, Christiana, Clarissa, Deborah, Diana, Dinah, Dorothy, Emily, Emma, Georgiana, Helen, Janet^, Joanna, Johanna, Judith, Julia, Kezia, Kitty*, Letitia, Nancy*, Ruth, Winifred>
E - Arabella, Celia, Charity, Clara, Cordelia, Dorcas, Eve, Georgina, Honor, Honora, Jennet^, Jessie*^, Joan, Joyce, Juliana, Juliet, Lavinia, Leah, Margery, Marian, Marianne, Marie, Mercy, Miriam, Naomi, Patience, Penelope, Philadelphia, Phillis, Prudence, Rhoda, Rosanna, Rose, Rosetta, Rosina, Sabina, Selina, Sylvia, Theodosia, Theresa
F - (selected) Alicia, Bethia, Euphemia, Frederica, Helena, Leonora, Mariana, Millicent, Mirah, Olivia, Philippa, Rosamund, Sybella, Tabitha, Temperance, Theophila, Thomasin, Tryphena, Ursula, Virtue, Wilhelmina
G - (selected) Adelaide, Alethia, Angelina, Cassandra, Cherry, Constance, Delilah, Dorinda, Drusilla, Eva, Happy, Jessica, Josephine, Laura, Minerva, Octavia, Parthenia, Theodora, Violet, Zipporah
H - Alberta, Alexandra, Amber, Ashley, Calliope, Calpurnia, Chloe, Cressida, Cynthia, Daisy, Daphne, Elaine, Eloise, Estella, Lilian, Lilias, Francesca, Gabriella, Genevieve, Gwendoline, Hermione, Hyacinth, Inez, Iris, Kathleen, Madeline, Maude, Melody, Portia, Seabright, Seraphina, Sienna, Verity
Men's Names
S+ John, William, Thomas
S - James, George, Joseph, Richard, Robert, Charles, Henry, Edward, Samuel
A - Benjamin, (Mother’s/Grandmother’s maiden name used as first name)#
B - Alexander^, Andrew, Daniel, David, Edmund, Francis, Frederick, Isaac, Matthew, Michael, Patrick~, Peter, Philip, Stephen, Timothy
C - Abraham, Anthony, Christopher, Hugh>, Jeremiah, Jonathan, Nathaniel, Walter
D - Adam, Arthur, Bartholomew, Cornelius, Dennis, Evan>, Jacob, Job, Josiah, Joshua, Lawrence, Lewis, Luke, Mark, Martin, Moses, Nicholas, Owen>, Paul, Ralph, Simon
E - Aaron, Alfred, Allen, Ambrose, Amos, Archibald, Augustin, Augustus, Barnard, Barney, Bernard, Bryan, Caleb, Christian, Clement, Colin, Duncan^, Ebenezer, Edwin, Emanuel, Felix, Gabriel, Gerard, Gilbert, Giles, Griffith, Harry*, Herbert, Humphrey, Israel, Jabez, Jesse, Joel, Jonas, Lancelot, Matthias, Maurice, Miles, Oliver, Rees, Reuben, Roger, Rowland, Solomon, Theophilus, Valentine, Zachariah
F - (selected) Abel, Barnabus, Benedict, Connor, Elijah, Ernest, Gideon, Godfrey, Gregory, Hector, Horace, Horatio, Isaiah, Jasper, Levi, Marmaduke, Noah, Percival, Shadrach, Vincent
G - (selected) Albion, Darius, Christmas, Cleophas, Enoch, Ethelbert, Gavin, Griffin, Hercules, Hugo, Innocent, Justin, Maximilian, Methuselah, Peregrine, Phineas, Roland, Sebastian, Sylvester, Theodore, Titus, Zephaniah
H - Albinus, Americus, Cassian, Dominic, Eric, Milo, Rollo, Trevor, Tristan, Waldo, Xavier
& Men were sometimes given a family surname (most often their mother's or grandmother's maiden name) as their first name - the most famous example of this being Fitzwilliam Darcy. If you were to combine all surname-based first names as a single 'name' this is where the practice would rank.
*Rank as a given name, not a nickname
+If you count Mary Ann as a separate name from Mary - Mary would remain in S+ even without the Mary Anns included
~Primarily used by people of Irish descent
^Primarily used by people of Scottish descent
>Primarily used by people of Welsh descent
I was going to continue on and write about why Regency-era first names were so uniform, discuss historically accurate surnames, nicknames, and include a little guide to finding 'unique' names that are still historically accurate - but this post is already very, very long, so that will have to wait for a later date.
If anyone has any questions/comments/clarifications in the meantime feel free to message me.
Methodology notes: All data is from marriage records covering six parishes in the City of Westminster between 1804 and 1821. The total sample size was 50,950 individuals.
I chose marriage records rather than births/baptisms as I wanted to focus on individuals who were adults during the Regency era rather than newborns. I think many people make the mistake when researching historical names by using baby name data for the year their story takes place rather than 20 to 30 years prior, and I wanted to avoid that. If you are writing a story that takes place in 1930 you don’t want to research the top names for 1930, you need to be looking at 1910 or earlier if you are naming adult characters.
I combined (for my own sanity) names that are pronounced identically but have minor spelling differences: i.e. the data for Catherine also includes Catharines and Katherines, Susannah includes Susannas, Phoebe includes Phebes, etc.
The compound 'Mother's/Grandmother's maiden name used as first name' designation is an educated guesstimate based on what I recognized as known surnames, as I do not hate myself enough to go through 25,000+ individuals and confirm their mother's maiden names. So if the tally includes any individuals who just happened to be named Fitzroy/Hastings/Townsend/etc. because their parents liked the sound of it and not due to any familial relations - my bad.
I did a small comparative survey of 5,000 individuals in several rural communities in Rutland and Staffordshire (chosen because they had the cleanest data I could find and I was lazy) to see if there were any significant differences between urban and rural naming practices and found the results to be very similar. The most noticeable difference I observed was that the S+ tier names were even MORE popular in rural areas than in London. In Rutland between 1810 and 1820 Elizabeths comprised 21.4% of all brides vs. 15.3% in the London survey. All other S+ names also saw increases of between 1% and 6%. I also observed that the rural communities I surveyed saw a small, but noticeable and fairly consistent, increase in the use of names with Biblical origins.
Sources of the records I used for my survey:
Ancestry.com. England & Wales Marriages, 1538-1988 [database on-line].
Ancestry.com. Westminster, London, England, Church of England Marriages and Banns, 1754-1935 [database on-line].
Girl therapy is learning a completely new language
Nat. She speaks more languages.
Ok, for fic writing purposes, who do you think would be more likely to fluently speak Spanish, Clint or Natasha?
what to do, with words unspoken?
drawn out silences and
sentences on the tips of tongues and
lips parted without a sound?
what to do, when voices die?
when phrases wither as lumps in throats and
aspiring monologues escape only as sighs?
words unspoken manifest and fester.
they rip and tear and burn from the inside--
set them free.
if not through the lips than from the fingers,
in uniform, tidy symbols or scrawled script.
set them free.
for words are nothing to be kept shuttered.
set them free.
~ On Poets and Writers and Painters and Love
Question, does anyones native language has a directly badass last name?, like, there is a guy i'm my school who's last name is "verdugo", literally, executioner
Me: my German knowledge is pretty good, if I may say so. I've been learning it for 12 years, after all.
German person: Hallo!
Me:

“Of course, it became apparent to me very quickly that he had no extraordinary talent at all. He has fought his way out of a number of tight corners by a simple combination of sheer luck and more talented friends. He is mediocre to the last degree, though as obnoxious and self-satisfied as was his father before him.
he’s sneak-complimenting hermione

Me when I pronounce one french word right “BONJOUR ITS ME HONHONHOON BAGUETTE”